
Prof. Scholz Miklas
University of Johannesburg, South Africa
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1316
by Hermawan Hermawan, Amin Safa’at, Nabila Arrizqi Annisa
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
The research paper delves into the implementation of sustainable architectural design practices at Puri Brata Resort & Gallery in Yogyakarta, Indonesia. The primary objective of the study is to analyze the impact of eco-friendly design principles on both the environment and visitor experience within the resort. Data collection for this research involved conducting a comprehensive survey among visitors to the resort, focusing on aspects such as air quality, temperature control, and overall visitor comfort. Additionally, data was gathered on the utilization of green spaces within the resort and the incorporation of local cultural values and aesthetics in the architectural design. The survey responses were then analyzed to evaluate the perceived impact of sustainable design elements on the guest experience and environmental sustainability. The findings of the research indicate that the integration of eco-friendly practices at Puri Brata Resort & Gallery has positively impacted various aspects, including improved air quality, efficient temperature control, and enhanced visitor comfort. The use of recycled materials, renewable energy sources, and green spaces has contributed to creating a harmonious and sustainable environment that enhances the overall guest experience. The study underscores the importance of incorporating sustainable design principles in architectural practices to create spaces that benefit both the environment and visitors. This research provides valuable insights for industry practitioners and policymakers looking to adopt sustainable design practices in the hospitality and tourism sector.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1381
by Scott. A. Lowe
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
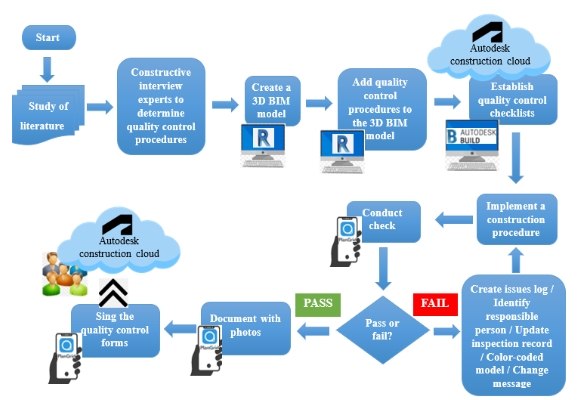
For new building construction, roofs typically have a large number of penetrations that are blocked out before the roof deck is poured. After the roof is poured, these penetrations need to be sealed temporarily to prevent rainwater entering the building. Unfortunately, it is all too common that the ad-hoc approach to sealing these openings results in penetrations left open to the elements. This results in water pouring into the building every time it rains. This paper shows examples of unsealed roof penetrations and of the subsequent damage caused. The penetrations relate to the work of several different trades, who may not place any priority on this issue. It is therefore suggested that this is a problem that the construction management team has to take charge of. At the very least, the roof should be inspected before impending rain events.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1451
by Xiaowei Wang, Keda Chen, Yuqing Zhang
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
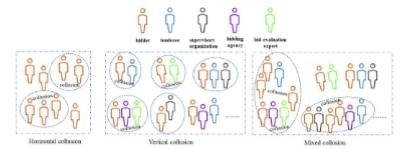
Policy measures are crucial for regulating collusive bidding and are integral to effective governance. However, current research lacks a comparative exploration of strategies to combat collusive bidding through policy. Therefore, this study aims to identify more effective countermeasures by examining policy variations between regions with low and high incidences of collusive bidding. Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) topic modeling, the study extracts key themes from these policies, while qualitative analysis highlights differences in approaches. It underscores that integrating electronic and information technology into bidding systems significantly reduces collusive practices. While increasing penalties can deter collusive bidding, achieving desired impacts requires thorough investigation and vigilant oversight. Additionally, strengthening external supervision enhances control over such activities. This study identifies critical governance strategies for addressing collusive bidding and advocates further research into more effective methods within the construction sector.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1811
by Reedhi Shukla, Sampath Kumar Pabbisetty, Satish Jayanthi, Kamini Janardhanan
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
Bridges are vital for linking communities and facilitating economic activity. However, in the face of disaster, like ship collisions pose a significant threat to bridge infrastructure, causing structural damage and potential safety hazards. Rapid and precise assessment of the damage is essential for effective emergency response and recovery operations. Remote sensing with near-real-time satellite imagery provides the disaster scenario. This paper presents a change detection using pre- and post-disaster satellite data for Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge to identify structural damage due to the collision of the ship with support pillars on 26 March 2024. Both optical and microwave satellite data were used from open data sources and analyzed based on geospatial techniques such as change detection and surface profiling. It is estimated that an 1100-meter span of bridge was affected due to this collision, which helped to estimate the damage and mobilize the rescue operations. It may need further validation from ground truth information. Hence, the current study emphasizes the potential of remote sensing satellite data to provide near-real-time impact on disaster analysis.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1440
by Yue Lyu
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
This study aims to reduce nitrogen emissions from residential buildings and establishes a prediction model for nitrogen emissions during the production of building materials. The calculation boundary, content, and method of nitrogen emission in the production stage of residential building materials are accurately analyzed. Based on the nitrogen emission data of 20 residential buildings in Guangdong, the composition and distribution characteristics of nitrogen emission in the production stage of building materials are analyzed. The coupling relationship between building design parameters and building materials’ nitrogen emissions is established using linear regression and ridge regression. 10 kinds of nitrogen emission prediction models based on the design parameters of residential buildings in the production stage of building materials were established and verified. The results show that the linear model M3, based on the number of floors above and below ground, the area width and depth, and the ridge regression model M5, based on the number of floors above and below ground, the area width and depth, and the total number of main functional rooms, have good fitting and prediction performance, respectively. The linear regression model M6, based on the number of floors above and below ground, the area width and depth, and the total number of rooms, has the best fitting and prediction performance. M3, M5, and M6 can accurately predict the nitrogen emission composition and distribution characteristics of building materials in residential building design and lay a foundation for future research on nitrogen emission evaluation and calculation methods and nitrogen emission reduction technology strategies.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1567
by Warda Jannat Juhin, Raihan Uddin Ahmed, H. M. A. Mahzuz, Md. Ariful Islam
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
In this paper, the torsional behavior of 8 beams in 4 categories with 2 different ultimate concrete compressive strengths (22.92 MPa and 43.47 MPa) was evaluated, and the best alternative of shear reinforcement pattern compared to the conventional non-welded rectangular stirrup beam (NRSB) was determined. 4 types of beams were modeled using SolidWorks, namely—Non-welded Rectangular Stirrup Beam (NRSB), Welded Rectangular Stirrup Beam (WRSB), Normal Welded Warren Truss-shaped Beam (NWWTB), and Flipped Welded Warren Truss-shaped Beam (FWWTB). The dimension and weight of reinforcement were kept the same for all beams. After simulating using ANSYS, it was seen that WRSB specimens had the largest torsional moment capacity, while NWWTB in normal orientation showed marginal improvement compared to NRSB.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1510
by Atef Badr
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
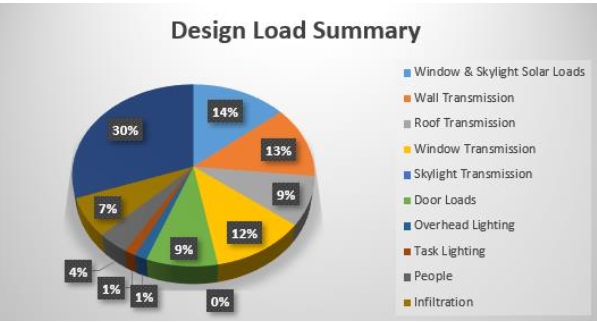
Energy plays a very important role in Egypt’s economic development, but the country has a gap between its produced energy and the demand of its growing population. Utilization of solar power systems in Egypt could help the country to close this gap and fulfil its national and international obligations. However, since 1980, the focus in Egypt has been on large-scale industrial solar projects. Limited attention is given to smaller systems for typical residential buildings. The aim of this research, therefore, is to highlight the potential of small residential solar systems (SRSS) in Egypt. With the huge number of residential buildings accommodating more than 115 million Egyptians, SRSS could be the unearthed gem of a sustainable source of energy in Egypt. The geographical location of Egypt and climate were used to generate solar data using the Global Solar Atlas application. The amounts of monthly and annual solar irradiations were calculated and analysed to decide the best orientation of the system (facing east, west, north, and south), identify the optimum tilt angle of the system, and determine the size of the solar panels. A case study was used to illustrate the procedures of designing SRSS for a typical residential building in Egypt. The results showed that a 26 kWp SRSS oriented facing the east with an optimum tilt angle between 15° and 30° could produce an annual total output of electricity more than the annual demand of the occupants of the studied residential building. Such a system would fit easily on the roof of the building. It was concluded that the installation of SRSS in Egypt could help the country meet the demand of its ever-increasing population if properly regulated, financed, and managed. It is recommended that Egypt develop and implement policies to make installations of SRSS an attractive choice among homeowners and investors by introducing encouraging incentives and creating a competitive market with affordable SRSS.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1342
by Hafnidar A. Rani, Mahdi Syahbana, Epi Noviana, Muhammad Hafidz Mubarak, Muhammad Shafly Aqsha
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
The assessment of building reliability is a critical aspect of the functional feasibility system, as outlined in the 1998 Technical Instructions of the Directorate General of Human Settlements. These assessments typically encompass architectural, structural, and utility criteria. This research aims to understand the role of consultants in evaluating the functional feasibility of buildings in Banda Aceh. Purposive sampling was employed with 11 respondents, considering factors such as education, legal, and technical expertise. Data analysis involved factor analysis using the KMO-MSA method and descriptive analysis using SPSS software. The results reveal that consultants play a crucial role in assessing the functional feasibility of buildings, particularly in terms of skill competency, integrity, and professionalism, with a significant emphasis on the suitability of the function and specifications of the requested buildings. Moreover, the legal factor variable emerges as pivotal in consultants’ activities, ensuring compliance with statutory regulations. This study underscores the importance of consultants in ensuring building reliability and adherence to stipulated provisions.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1247
by Mario Luis Chew Hernández, Leopoldo Viveros Rosas, Raúl Gómez Gómez-Tagle
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
In the construction industry, the signing of contracts between contractors and clients is a common practice. The entities signing these contacts have vastly different objectives in the context of the project: the contractor is motivated by the achievement of profit, while the client has objectives that can be economic, aesthetic, related to completion time, etc. According to negotiation theory, the greater the difference between the objectives of the sides, the better the contracts that can be achieved in the negotiation. Therefore, the analysis of a contractor-client negotiation in the building industry should be based on a complete understanding of the objectives of the sides. Kenney’s Value-Focused Thinking (VFT) provides a framework on which such understanding can be achieved. This paper presents a VFT-based methodology to analyze the contractor-client negotiations in the context of construction projects. The methodology is illustrated by analyzing, in retrospective, the negotiation between a construction company and a client regarding the construction of a dome for a church. The results show the usefulness of analyzing the negotiation from the point of view of the sides’ objectives.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1503
by Sameer Jain
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
This research examines the Internet of Things (IoT), a fast-developing technology that has transformed several industries, through bibliometric analysis of the building and construction sector. The current state of research, its features, and possible future paths are evaluated using the Scopus database. A thorough search of the literature conducted with Scopus produced a total of 2070 publications published between 2004 and 2022. Over the past five years, the number of IoT articles in the construction industry has significantly increased, according to the research. The study found that the top five countries for publications on this issue were China, Hong Kong, India, Portugal, and Sweden. The data suggests that a number of topics, such as energy management, construction automation, and smart buildings, have attracted a lot of attention. Additionally, the survey found that wireless networks and sensors were the IoT technology most frequently employed in the construction sector. The paper also makes recommendations for potential research directions, including the employment of cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence, as well as the application of IoT in the building sector. The study’s results shed light on market trends, unmet needs in the field, and prospective directions for Internet of Things applications in the construction sector.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1314
by Nathalie Tornay
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.2, 2024;
In this paper, we develop a global vision of environmental impact with alternative building materials in architectural design. A bibliometric study is based on 1827 scientific research publications on alternative materials produced between 1998 and 2022. More than 90% of these documents have been published in the last ten years. This bibliometric study goal is to develop a systemic approach for the characterisation of alternative solutions in the context of scarce resource context and climate change. This study highlights three different approaches: 1) an ‘integrative’ approach that develops an implementation approach combining environmental concerns and design teams’ own working methods in the selection of materials; 2) an ‘additive’ approach that selects some environmental criteria (carbon footprint and energy consumption) in addition to implementation issues; 3) a ‘subtractive’ approach that focuses solely on implementation issues.