
Prof. Scholz Miklas
University of Johannesburg, South Africa
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1739
by Moustafa Wassouf , Jamal Omran, Ali Kheirbek
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
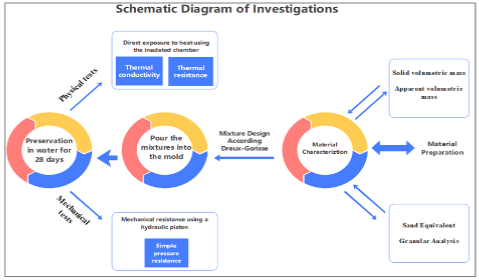
Green concrete, also known as sustainable concrete, is a building material that aims to reduce environmental impact by using natural, recycled, or sustainable materials in its production. One way to achieve sustainability in concrete is to replace cement with pozzolanic materials, which not only reduces the carbon footprint but also improves the performance of concrete and reduces its cost. This study aims to use natural materials that can partially or completely replace cement and conventional aggregates in concrete mixes. pozzolanic gravel (GPoz) replaced coarse aggregate, basaltic sand (SBas) and pozzolanic (SPoz) replaced fine aggregate, while ground pozzolana (PN) replaced cement. This work focuses on the experimentation and simulation of concrete mixes using the four abovementioned materials. 36 cubes were cast to conduct the thermal conductivity test by direct exposure of concrete samples, where an insulated thermal chamber was designed from thermal bricks, equipped with a heat source from the bottom and an empty space for the tested sample from the top, and then the resistance test on simple pressure was conducted for the cubic samples at the age of 28 days. Pozzolanic aggregate, when used in combination with basalt sand, showed greater thermal resistance compared to conventional concrete. Even with the replacement of 50% of the cement with ground pozzolana, we notice an increase in resistance of more than 11%, but with the replacement of basalt sand with pozzolana sand, we notice an increase in thermal resistance of more than 53%. As for the mechanical properties represented by resistance on simple pressure, we notice an acceptable decrease in resistance when replacing cement with pozzolana, with the exception of mixtures containing aggregates and pozzolana sand together, where replacing 50% of the cement with pozzolana increases the resistance on simple pressure by more than 46.4%.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1459
by Mansir Dodo, Abdulmalik Badamasi, Kabir Ibrahim, Narimah Kasim, Zairra Mat Jusoh, Suleiman Musa Garba, Sanusi Gambo
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
Plastic bottles package a multitude of commodities consumed worldwide. Upon consumption of the commodity, the disposed plastic bottles accumulate as waste, having impacts on both the aquatic and terrestrial environment. In a bid to convert such waste to wealth, plastic bottles are creatively reused for different applications, such as pedestrian bridge boats and street furniture, amongst others. Another application of reusing plastic bottles is their serving as building blocks for housing construction. Reports and research in Nigeria confirm the proliferation of plastic bottles littering the environment, which if reused in housing construction has the potential to contribute to achieving both UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) 11 (making human settlements sustainable) and 12 (ensuring sustainable consumption and production). Although Nigeria is traced to being the first country in Africa to reuse plastic bottles in housing construction, not much research output exists from practitioners’ experience on the potentials of reusing plastic bottles as a sustainable construction material as practiced in countries like Vietnam, India, and the Philippines, among others. As such, this study investigates the potential factors driving the practice of reusing plastic bottles in Nigeria with a view to ascertaining the satisfaction derived from the practice for sustainable housing construction. Primary data was collected using a structured questionnaire from 41 respondents identified as having experience in using plastic bottles in construction (5 staffs of Awonto Konsult as well as 36 staffs of Brains and Hammers Construction). Data was analysed descriptively using both IBM SPSS Statistics 23 as well as MS Excel to compute the Mean Score as well as the Relative Satisfaction Index (RSI). Only 30 questionnaires were successfully retrieved and fully answered. Amongst the 10 potential factors studied driving reusing plastic bottles, results show that almost all respondents tend to be ‘satisfied’ with both ‘strength and stability’ (having a Mean Value of 4.70 and RSI of 0.94) as well as ‘durability’ (having a Mean Value of 4.50; RSI of 0.90) of buildings built with plastic bottles. These two factors recorded the highest ‘satisfaction’ ratings, leaning towards ‘very satisfied’. Regarding the factor ‘fire resistance’ of buildings built with plastic bottles (having a Mean Value of 3.40; RSI of 0.68), results reveal that 50 percent of the respondents are ‘unsure’ if it is a satisfactory factor driving reusing plastic bottles or not. The study found that the satisfaction ratings of technical and environmental factors have higher appeal to respondents compared to health and safety and also financial factors. It is recommended that Awonto Konsult and also Brains and Hammers Construction invest more in information related to the fire resistance of plastic bottles used in construction because fire outbreaks pose great threats to buildings. Equally, wider empirical research on plastic bottle wastes, if undertaken, could support the development of policies for waste management, particularly in developing countries. This research has the potential to convert waste into wealth in a bid to minimising environmental impacts of disposed plastic bottles as well as contribute to sustainable materials, particularly for rural housing. Since this study was based on a survey, experimental studies of potentials driving the reuse of plastic bottles in housing construction will reveal results that could enable more sustainable housing construction in Nigeria.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1509
by Yonatan Getachew Zegeye, Mohammadzen Hasan Darsa
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
Construction projects are inherently fragmented and complex, influenced by various risk factors that can significantly affect both costs and schedules. Identifying and prioritizing these risk factors is crucial for enhancing project management and achieving successful outcomes. This research aimed to identify the most significant risk factors affecting construction projects in terms of cost and schedule performance within the Dire Dawa City Administration and Harari Region, considering the perspectives of contractors, clients, and consultants to provide actionable insights for risk mitigation. A comprehensive literature review and pilot survey initially identified 41 risk factors, which were refined through an iterative process to select 42 factors for a detailed questionnaire survey. Additionally, semi-structured interviews were conducted to gather qualitative insights. Data analysis employed mean ratings to identify the top ten risk factors, utilizing Probability Impact (P-I) Matrix and regression techniques to assess each factor’s significance. The results highlighted six critical risk factors among the ten identified as most impactful: inflation, increases in material prices, exchange rate fluctuations, payment delays, poorly coordinated design, and material delays. The findings indicated strong positive correlation values (R = 0.800 and R = 0.840) in both models, suggesting that as one variable increases, the other tends to increase as well. These insights provide valuable guidance for project managers, emphasizing the need to focus on these critical risk factors to improve cost and schedule management, ultimately enhancing project outcomes and minimizing cost overruns in the region.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1651
by Serkan Yildiz
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
In a construction project, a significant part of the costs and construction process is controlled by materials. It is possible to significantly increase productivity at the construction site with successful material management. In this study, first, a comprehensive literature review on material management processes was conducted and how material planning, material procurement, material acceptance and inspection, storage and inventory control, material handling and productivity issues were discussed in the literature was reviewed. Then, the contribution of nine criteria regarding material management to productivity was evaluated through surveys conducted at different construction sites. The study revealed that there were significant differences between the participants’ evaluations according to their gender, education level, profession and construction site size. However, according to general evaluations, the most important criteria were found to be proper storage of materials, identification of critical materials and proper handling of materials. It is evaluated that the study will be a guide for stakeholders in the establishment of material management processes.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1834
by Mo Shi, Minwoo Choi, Yeol Choi
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
With the ongoing acceleration of the urbanization process, a large portion of the population is concentrated in urban areas, leading to significant issues with living space. The increasing number of vehicles necessitates more parking space, and the phenomenon of urbanization requires new building structures that can accommodate this need. As a result, there has been a rise in Piloti-type RC (reinforced concrete) structures, particularly in the Republic of Korea. These structures utilize their open ground floors for various purposes such as parking, storage, and social spaces, adding functional diversity to buildings and receiving positive reviews for these advantages. However, the open ground floor can potentially create security vulnerabilities if not adequately secured or monitored. This was evident during the Pohang earthquake in 2017 when numerous Piloti-type RC structures sustained more severe damage than conventional RC structures. Therefore, numerous previous researchers have emphasized the importance of ensuring structural safety in Piloti-type RC structures. In this research, the structural designs under the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport of the Republic of Korea were used as a basis for simulation in SAP 2000. The focus was on comparing the structural performance of a typical Piloti-type RC structure with and without the Piloti-type design using nonlinear pushover analysis. The findings of this research are expected to provide a clear understanding of the differences between Piloti-type RC structures and non-Piloti-type RC structures. Additionally, based on the specific characteristics of Piloti-type RC structural vulnerabilities identified through nonlinear pushover analysis, this research is anticipated to serve as a valuable reference for reinforcing existing Piloti-type RC structures to better resist seismic activities, thereby reducing human casualties and economic damage resulting from seismic events.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1980
by Junwei Chen, Jiang Jun, Yuqiang Feng, Nan Jiang
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
As a mainstay industry of national economy, construction brings a country huge benefit, et along with significant amount of pollution to environment. In the age of sustainable development, green building (GB) can greatly reduce pollution caused by the construction industry. To study the evolution of stakeholders engaged in China’s green building implementation, this paper designed a three-party game model including government, developer, and consumer, analyzed the stability of the model and obtained the evolutionary stability strategy. This paper also used green building data in China to conduct numerical simulation, including sensitive analysis to explore key factors affecting the game subjects, and phase diagrams and bifurcation diagrams to analyze influence of parameter change to the evolutionary stabilization strategy (ESS). The results show that (1) in the long term, the government will choose the regulatory strategy when the cost of government regulation is below one-third of the financial subsidy; (2) the probability of developers and consumers choosing the green building strategy is negatively correlated to the cost and positively correlated to the benefit; (3) the primary determinant behind customers’ decision to purchase a green building revolves around the enhanced quality of life that such buildings offer.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 2054
by Ali Hassan, Ahmad Riaz
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
Labor productivity is an essential component for the effective execution of a project. This research aimed to determine the cause of the labor crisis in the construction industry of developing countries. This research focuses on numerous aspects such as the trades of shorted skilled labor, the shortage causes, the effects of the shortage of skilled labor in industry, the characteristics that skilled labor should have, and the mitigation strategies. The field survey conducted included twelve trades, sixteen causes, nine effects, and eleven characteristics of skilled labor. The top three trades with a significant shortage are heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) installer technicians, wood carpenters, and glazier/aluminum workers. The top three causes accountable for the labor shortage are irregular and low wages, poor training, and economic change. Extension in the duration of the project and Errors during construction emerged as the top two effects caused by a shortage. The top three characteristics of skilled labor are technical competence, in-depth knowledge of handling tools and equipment, determination, and persistence. The survey concluded that offering advantageous wages and benefits, providing opportunities for advancement and professional development, and establishing a positive work environment can effectively reduce the effects of labor shortages by recruiting and retaining skilled individuals.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1625
by Opakrwoth Chrispus, Abdulsalam Ibrahim Shema
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
Formal settlements refer to those settlements that comply with legal and regulatory frameworks, while informal settlements, commonly known as slums, arise without official sanction and often lack basic services and infrastructure. Informal settlements are an inherent reality that are integral parts of the urban centers in most developing nations such as the capital city of Uganda, Kampala. Currently, the city is experiencing numerous urban challenges such as inadequate housing, overcrowding, crime, and limited access to basic social services. These challenges have adverse social, economic and environmental impacts. Formal settlements typically provide basic services in proclaimed townships. By integrating formal standards into informal contexts, regeneration can conceptualize meeting formal necessities such as decent housing. This research explores the intersection of formality and informality within the urban center of Kampala, specifically in Katwe district. The research aims to explore regeneration actions in Katwe, aiming to enhance quality of living. This goal will be pursued through strategic approaches that enhances social equality and identifying social generators of activities for improved quality of life; Defining components of housing typologies for enhanced individual quality of life through self-built sustainable constructions; Establishing a unifying design focal point in the neighborhood to cultivate identity. The adopted research methodology for this exploration was developed based on a mixed-method research approach, employing procedures such as document analysis and observational study to gather necessary information from Katwe informal settlement in Kampala.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1965
by Duong Thi Ha, Vu Hoa Ky, Trinh Van Cuong
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
As Vietnam’s construction industry accelerates modernization, carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) emerges as a pivotal material for sustainable, high-performance infrastructure. With its lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly durable nature, CFRP enhances structural longevity, minimizes maintenance, and reduces environmental impact, aligning with global sustainability goals. Widely applied in bridges, high-rise buildings, and coastal structures, CFRP addresses Vietnam’s unique environmental challenges, providing resilience against humidity, chemical exposure, and seismic activity. However, high costs and limited expertise in CFRP application remain obstacles. Strategic investment in cost-reducing technologies and workforce training is crucial for widespread adoption. As CFRP’s benefits become increasingly recognized, Vietnam’s construction sector has the opportunity to lead in sustainable infrastructure, creating lasting, eco-friendly solutions that reflect the country’s commitment to both innovation and environmental responsibility.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 2375
by Guolin Li
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) is vital for the well-being, health, and productivity of people in architectural spaces. As the awareness of the importance of IEQ has grown, there has been significant development and research in this field. This article aims to provide an overview of the recent trends in IEQ research in architecture. It emphasizes the significance of creating healthy and comfortable indoor spaces and highlights how IEQ can impact occupants’ well-being and productivity. The article discusses various factors that influence IEQ, such as air quality, thermal comfort, lighting, and acoustics. Additionally, it examines the advancements in design strategies and technologies aimed at improving IEQ. Finally, the article concludes by identifying future research directions and potential areas of innovation in the field of indoor environmental quality. This review highlights that indoor environmental quality (IEQ) has become a central focus in architecture, with research underscoring the significance of creating healthy and comfortable spaces for occupants. Future studies should focus on integrating smart technologies, health-centered design, addressing the impacts of climate change, and enhancing the multi-sensory experience to further improve IEQ and promote human well-being.