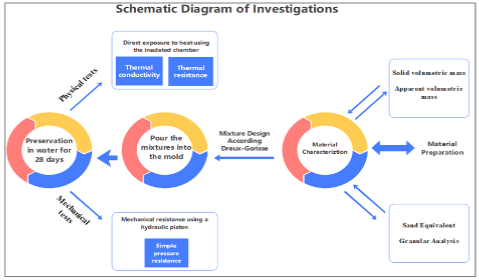
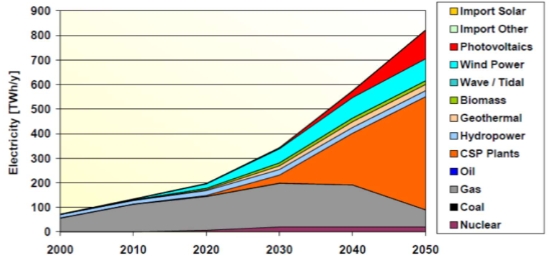
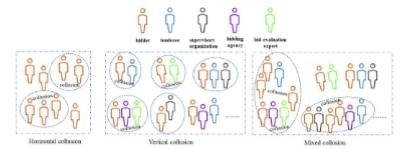
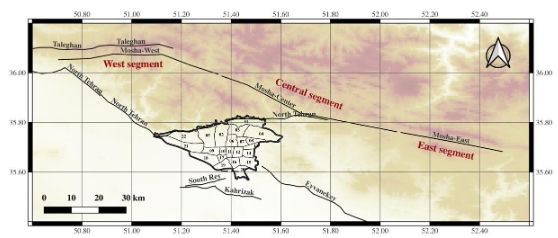
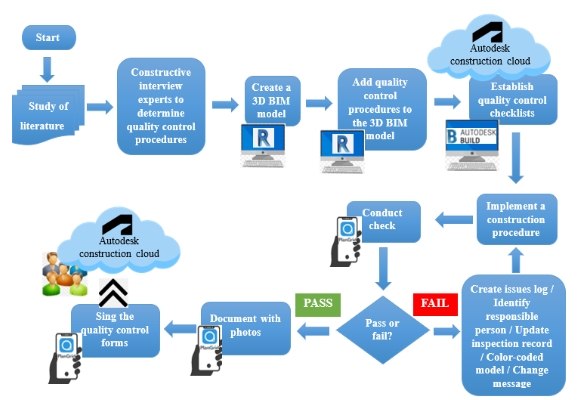
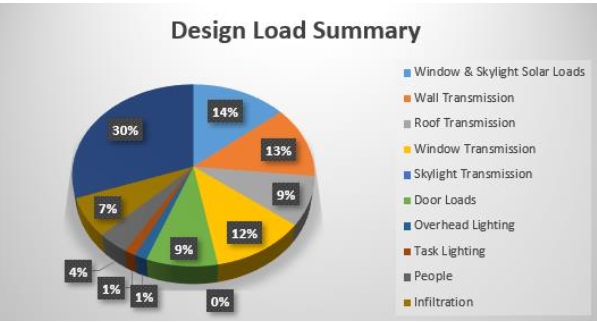
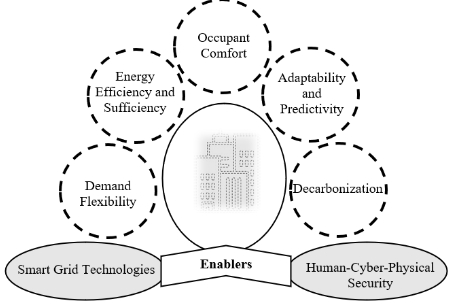
Description
Building Engineering (BE, eISSN: 3029-2670) is a scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on building science, building engineering, and architecture. We encourage researchers to publish their innovative ideas and results on numerous elements of buildings, such as construction, plan, operation, performance, maintenance, and degradation. The scope of this journal encompasses a wide range of topics relevant to the built environment, and authors are encouraged to read the Focus and Scope of the journal.
Latest Articles
-
 Open Access
Open AccessArticle
Article ID: 2207
CFD-based comparative simulation analysis of flow field under different natural ventilation boundary conditions in the roomby Yuanyuan Fu, Bin Zhao
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
In order to achieve reasonable indoor layout design, reduce building energy consumption and better meet human body thermal comfort requirements, flow fields under different natural ventilation conditions are compared based on computational fluid dynamics (CFD) in this paper. Firstly, a theoretical model of the indoor flow field under six different ventilation conditions is constructed, and boundary conditions, wall functions and meshing structure are confirmed. Simulation analysis is carried out for six different working conditions. Through comparative analysis, it is concluded the window opening location should be located in the center, and the direct airflow through the convection field is evenly distributed, and the direct airflow is conducive to the improvement of indoor cleanliness. In addition, when organizing natural ventilation, the window orientation is inclined to the dominant wind direction in summer by about 45° angles, it can improve the ventilation effect. And by analyzing temperature contours, 45° angles can better meet people’s needs about temperature: 18 ℃–26 ℃. When temperature contours’ temperature is above people’s comfortable temperature in specific rooms or places, mechanical ventilation and evaporative cooling can be combined. Research results can not only significantly improve the quality of living and working environments, but also help promote the development of green buildings and achieve energy-saving and emission reduction goals.
show more -
 Open Access
Open AccessArticle
Article ID: 1703
Impact of activity time stochasticity on critical paths and their completion probabilities in construction projectsby Saurabh Gupta, Riya Catherine George, Deepu Philip, Syam Nair
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
Accurate planning and project control activities are essential in ensuring the timely completion of construction projects. Even though the classical scheduling techniques like Gantt charts, critical path method (CPM), program evaluation and review technique (PERT), etc., are well-designed and can effectively support construction scheduling functions, they do not account for the variability in activity times arising out of the random/stochastic nature of the activities involved. The study utilizes a simulation-based approach to identify the impact of variability in activity time durations on critical paths and on the probability of timely completion of construction projects. The effectiveness of four different probability distribution functions, namely uniform, triangular, bound exponential, and unbound exponential, in capturing the stochasticity of activity times in construction projects was also evaluated as part of the study. A MATLAB-based simulation framework was developed to sample random durations of project activities and compute various project scheduling parameters based on PERT assumptions. Activity time variability was introduced in the network by extending pessimistic time (tp) by up to 50%. Observation in the study suggests that for projects that experience delays during execution, allocating additional resources to the preassigned critical path may not always be effective in addressing these delays. Instead, dynamic corrective measures (time extensions, resource allocation, etc.) that consider all possible scenarios of project completion and can account for any possible changes in critical path due to the incurred delay may be adopted to ensure a higher probability of project completion within the revised schedule. Exponential bounded distribution was found to provide a more realistic estimate of project completion time with a high probability of timely completion of construction projects. The study also suggests exponential unbound distribution to be effective in simulating worst-case scenarios encountered in construction projects. Future research could validate this approach on real projects and use machine learning to automate scheduling adjustments for delays.
show more -
 Open Access
Open AccessArticle
Article ID: 2105
Digital poverty in quantity surveying practiceby Iyanu Simeon Michael, Olusola Festus Akinradewo, Taiwo Fadeke Adegbembo
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
Background: Digitalization has profoundly impacted the construction sector, offering tools and technologies that promise increased efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration. Nevertheless, the integration of these digital solutions, notably Building Information Modeling (BIM), can be impeded by a set of fundamental barriers known as enablers of digital poverty. These enablers encompass a range of challenges that quantity surveyors face in Lagos State when attempting to embrace BIM and other digital tools. Objective: The objective of this study is to pinpoint, classify, and assess the factors that enable digital poverty when it comes to implementing BIM within the community of quantity surveyors in Lagos State, Nigeria. By understanding these enablers, stakeholders can develop targeted strategies to alleviate digital poverty and promote digital inclusion in the field of quantity surveying. Methods: A quantitative research method was utilized, employing a questionnaire survey to collect information from quantity surveyors in Lagos State. The questionnaire used in the study was designed to collect demographic data and evaluate the factors contributing to digital poverty. The collected data were analyzed using the mean item score and subjected to exploratory factor analysis (EFA) to uncover hidden groups or patterns among these contributing factors. Results: The EFA exposed five distinct clusters of enablers of digital poverty: Exploration Enablers—Factors related to creating an enabling environment for digital adoption, including limited financial resources, inadequate institutional arrangements, and lack of awareness; Incognizant Enablers—Factors reflecting a lack of knowledge and awareness, such as erratic power supply and insufficient government support; Compliance Enablers—Factors associated with the challenges of complying with new digital practices, including resistance to change from traditional methods and the scarcity of BIM specialists; Infrastructural Enablers—Challenges linked to infrastructure, including high costs of investment and software/hardware upgrades; and Automation Enablers—Factors related to the adoption of automated processes, such as an unsupportive organizational culture, lack of experience and knowledge, and inadequate support from senior management. Conclusion: This research provides a comprehensive understanding of the enablers of digital poverty in BIM implementation among quantity surveyors in Lagos State. It highlights the multifaceted characteristics of these challenges and underscores the importance of addressing them to promote digital inclusion and leverage the advantages of digital technologies within the construction sector. The identified enablers can serve as a foundation for policymakers, organizations, and communities to develop targeted interventions aimed at reducing digital poverty and fostering a digitally inclusive environment for quantity surveyors in Lagos State.
show more -
 Open Access
Open AccessArticle
Article ID: 2598
Effect of chemical treatments on the mechanical and physical performance of corn straw fibers in cement mortarby Bo Peng , Zulhazmee Bin Bakri
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
This study investigates the effects of water, acetic acid (CH3COOH), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) treatments on the physical and mechanical properties of corn straw fibers in cement mortar. The use of natural fibers in cement composites offers a promising approach to reducing reliance on synthetic materials and utilizing agricultural byproducts. Chemical treatments like NaOH and CH3COOH improve fiber-matrix bonding, which is critical for enhancing the mechanical properties of the composites. NaOH treatment resulted in the most significant improvements, with surface roughness increasing by 104.8% and compressive strength reaching 52.8 MPa at 1.5% fiber content after 28 days. CH3COOH treatment boosted early-stage flexural strength, achieving 6.75 MPa at 7 days, but its long-term effect was limited. Water treatment showed minimal impact on fiber performance. These results indicate the potential for NaOH-treated fibers to enhance the strength and durability of cement-based materials.
show more -
 Open Access
Open AccessReview
Article ID: 2100
A review on significance of thermal comfort in educational facilitiesby Huda Riaz, Ahmad Riaz, Amna Iqbal, Norheen Amina, Sunera Imtiaz
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
Climate change and the urgency of decarbonizing the built environment drive technological innovation in delivering thermal comfort to occupants. Studies have shown that thermal discomfort can lead to a decline in students’ cognitive function, motivation, absenteeism, and a decrease in instructors’ work performance. This article reviews significant changes, developments, and trends in thermal comfort research for educational facilities classrooms. This study summarizes research regarding the importance of environmental comfort in education facilities, different climatic regions, and various parameters that play a vital role in determining thermal comfort. The investigation of the current literature showed that researchers focused on different issues, adopting diverse models and indices to investigate thermal comfort in classrooms. Indeed, even if the environmental conditions comply with standards, in several cases, a prolonged stay indoors affects the health and productivity of students. However, it is important to focus on students’ preferences in different regions, climates, and educational stages to create healthy and human-centered buildings. It is also clear that current research trends mainly focus on cold regions of Europe, while, by educational level, secondary-stage classrooms are the least investigated; thus, further investigation is needed. Therefore, an integrated approach that considers both the positive and negative effects of indoor exposure is needed, including the individual preferences and needs of occupants in the least researched regions, such as Asia and Africa.
show more -
 Open Access
Open AccessArticle
Article ID: 1946
Multivariate optimization of mechanically ventilated photovoltaic double-skin façade system for the cold conditions of composite climate zoneby Sajan Preet, Sanjay Mathur, Jyotirmay Mathur, Stefan Thor Smith, Himanshu Saini
Building Engineering, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
Assessing the performance of a multi-storey building equipped with a mechanically ventilated photovoltaic-double skin façade (photovoltaic-DSF) system during cold weather conditions is crucial. This is because the demand for heating in buildings rises as outdoor temperatures decrease. This study formulates and verifies mathematical models to evaluate the energy performance of a building integrated with a mechanically ventilated photovoltaic-double skin façade (photovoltaic-DSF) system in Jaipur’s cold climate, which is part of India’s composite climate zone. The system was installed and observed during the winter months (December to February). The experimental design utilised a Taguchi L25 orthogonal array, considering variables such as air cavity thickness, air velocity, and photovoltaic (PV) panel transparency. Based on experimental findings, multiple linear regression analysis was used to predict three key performance metrics: The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), photovoltaic panel electrical output, and indoor daylight illuminance, all as influenced by the design parameters. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) confirmed the statistical significance of these relationships, and the model demonstrated a strong correlation with field measurements (R2 > 0.90), validating the accuracy of the developed mathematical correlations. The analysis reveals that a photovoltaic DSF system integrated into a multi-storey building, featuring a photovoltaic panel with 50% transparency, an air velocity of 5 m/s, and a 50 mm air cavity, achieves maximum energy performance under cold climate conditions in a composite climate. These insights can help in designing energy-efficient photovoltaic-DSF systems specifically optimised for winter conditions in composite climate zones.
show more