
Prof. Scholz Miklas
University of Johannesburg, South Africa
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 470
by Nazila Kheirkhah, Reza Alikhanzadeh, Ozhan Musavi, Ali Aghajani, Erfan Firuzi
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
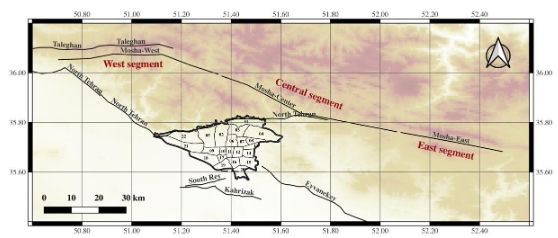
This paper presents the results of a study carried out to assess probable seismic loss in terms of damage to the residential buildings and the number of fatalities in the case of the Mosha Fault seismic scenario in Tehran, Iran. Accordingly, seismic risk components (including seismic hazards, exposure models, and fragility curves) are evaluated. The stochastic finite-fault method with dynamic corner frequency is applied for quantifying ground motion values. The results show that PGA on the soil surface could range between 0.1 g and 0.45 g. Then, a reliable model of building exposure by analyzing census data from Tehran is compiled. This model included 19 different classes of buildings and is used to evaluate the potential damage to buildings from seismic scenarios. The results indicate that the median damage ratio from 100,000 iterations for the whole of the city is about 6% ± 1.54%. The study found that the central and eastern parts of Tehran are the most vulnerable areas, with an estimated 15,952 residents at risk of losing their lives in this scenario. This is equivalent to 0.2 percent of the total population of Tehran. The findings from this study can be used by local authorities to provide appropriate emergency response and preparedness plans in the case of the Mosha Fault seismic scenario.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 561
by Nor Aqilah Haji Juffle, Md Motiar Rahman, Rajul Adli Asli
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
Buildings account for the highest carbon dioxide emissions during their operation stage, primarily due to high energy use for heating, cooling, and lighting, which in turn contribute to global warming and climate change. Such impact can be considerably reduced through crafting sustainable design (SusD) in buildings. So, availability of relevant information, professional guidance to clients, and appropriate decision-making are crucial. A study summarized the findings from a questionnaire survey conducted in Brunei with 122 responses. The results revealed that architects, consultants, and government are more important stakeholders to assist with SusD adoption, while clients and developers are important stakeholders in decision-making. The results appreciate the roles of clients and architects to a higher degree, despite a comparatively higher number of private projects in Brunei with relatively more influence of contractors. This was interpreted as having a good degree of awareness of the survey participants towards the role of SusD and who actually can better contribute to SusD adoption. However, the outcome also revealed inconsistent perception among the respondents, both within and between different groups based on their affiliations and nature of job. This inconsistency implies the need for appropriate training or education to enhance awareness of SusD, make pertinent information available, and develop appropriate skills.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1132
by Mohamed Shaban, Bassel Al-Hassan, Alaa Shekh Mohamad
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
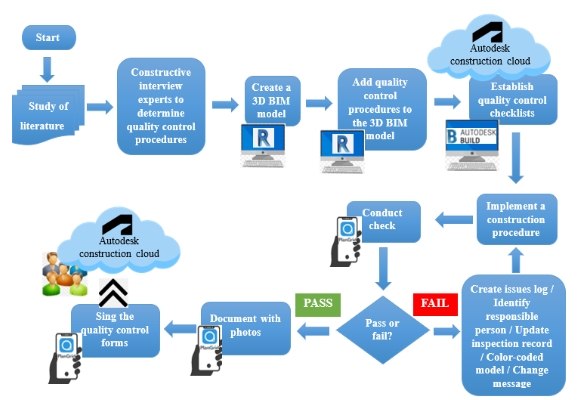
The quality of construction projects significantly impacts social and economic development. However, low quality and project failure often result from factors such as lack of quality procedures, poor communication, task coordination, and inefficient progress monitoring. This research aims to improve the efficiency of the construction phase by creating quality control checklists for processes and enhancing quality management through a collaborative digital environment integrating building information modeling (BIM) and cloud computing. Expert constructive interviews were first conducted to define a construction process quality control procedure to be linked to the 3DBIM model and then transition to a collaborative cloud environment (Autodesk Construction Cloud). An actual instance in Latakia City (Syria) demonstrated that the proposed methodology improves the efficiency and effectiveness of quality management during the implementation phase. It does so by offering a robust database, enhancing on-site quality information extraction from BIM models using smartphones, documenting defects and entering inspection data directly into a shared digital environment, and making it easier to track corrective actions and feedback. This facilitates constant and organized access to current data, reducing errors and rework, saving money and time, and enhancing decision-making speed and effectiveness. The search recommends the necessity of strict laws to adhere to quality procedures and the importance of providing infrastructure for digital transformation in quality management.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 509
by Ayman Mashali, Ahmed Eltantawy
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
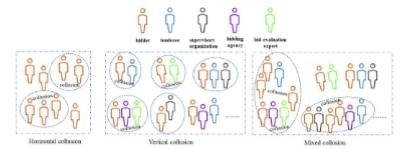
Purpose: The construction industry is a complex environment, it is facing massive challenges, especially on megaprojects, due to the huge construction development and stakeholder management (SM). This paper seeks to explore, investigate, and assess the methods for analysing and engaging stakeholders on construction megaprojects to overcome stakeholder management problems and enhance performance. Methodology: The quantitative methodology is adopted in this research; a questionnaire survey is carried out among big construction firms in Qatar, with a 59% response rate. Quantitative data analysis was conducted using the statistical package for social science (SPSS) software. Findings: This paper investigated and assessed the common methods for analysing and engaging stakeholders on construction megaprojects, where they come together more integrative. Hence, this will boost their chances of reaching higher levels of success and project effectiveness. Lastly, the findings are foreseen to aid project managers in adjusting their strategies when considering future implementation plans via a broad picture and understanding of SM and their relationships in CMPs. Practical implications: Investigating and assessing the methods for analysing and engaging stakeholders is expected to assist project managers in improving projects’ performance and completing construction within the predefined time and cost. Besides, it enhances and strengthens the present body of knowledge in SM study domains and provides a starting point for practitioners and academics. Originality: This study contributes significantly by investigating and assessing the methods for analysing and engaging stakeholders in MCPs. Moreover, the findings are important for all concerned project stakeholders and are considered as a roadmap for effective stakeholder management in MCPs.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1190
by Fathi M. Layas, Vail Karakale, Ramadan E. Suleiman
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
Earthquakes in some countries worldwide cause loss of lives and properties. In Libya, the design of structures to resist earthquake forces was based on a paper published by Mallick in 1976. In 1977, and after small changes in the earthquake zoning map of Libya, the ministry of housing, at that time, adopted it as a draft code of practice for the design of structures to resist earthquake forces. With Benghazi city undergoing significant rehabilitation and development programs, including major national projects, there is a pressing need to estimate updated probabilistic seismic hazard maps and design response spectra specific to the city. This study presented updated probabilistic seismic hazard ground motion for Benghazi city, considering different return periods and accounting for peak ground acceleration (PGA) values with various soil conditions. Proposed design response spectra for Benghazi City unveil substantial PGA amplifications in soft soil areas.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1226
by Bogdan Felix Apostol, Stefan Florin Balan
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
The paper highlights the performance of the seismic isolation devices installed on retrofitted buildings in reducing the seismic response when subjected to earthquakes. Two buildings from the beginning of the XXth century in Bucharest are chosen from many more, monitored over the city area. We discuss the response of these base-seismic isolated structures, relying on good quality data acquired from the recent strong earthquake (3 November 2022, MW = 5.0). Elastic response spectra computed from recordings at two levels of each structure are used, placed under and right above the isolating layer. At one building, the existence of previous recordings and the particularity of the sensors allow a comparison with the other two relatively recent medium-intensity earthquakes. The assessment is carried out in terms of maximum acceleration amax, measured at certain levels in each structure, spectral acceleration amplitude SAmax, and spectral-peak corresponding period. We find that the base-isolation methodology is effective in reducing the response of the building right above the isolating layer, an observation valid for both structures, all components of the recordings, and spectral acceleration values. Moreover, the outcomes from the modal evaluation performed prior to rehabilitation and the seismic isolation process are presented by pointing out a higher newly acquired fundamental period of the isolated structures.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1231
by Muthuraman Subbiah, Hafiz Zafar Sharif, Sivaraj Murugan, Kumar Ayyappan
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
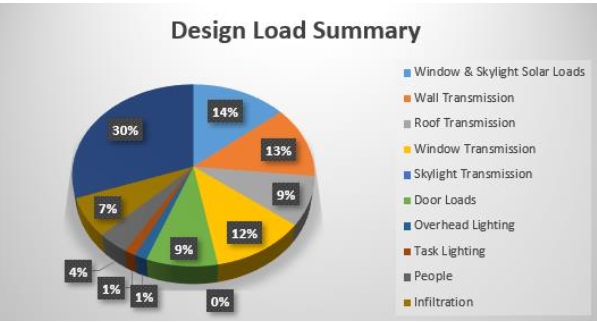
The building sector is the predominant consumer of primary energy globally. The building sector accounts for around 40% of global energy production. Net Zero Energy Buildings (NZEBs) are highly suggested by energy experts as an effective option to alleviate the strain on primary energy sources caused by the building sector. The disparity between energy performance predictions provided during the design phase and the actual energy performance of residential buildings is mostly attributed to a limited comprehension of the components that influence energy consumption and the constraints of whole building simulation software. The objective of this research was to perform a comparison analysis of the expected and actual energy consumption of a prototype net-zero energy house built at the University of Technology and Applied Sciences in Muscat. The Hourly Analysis Programme (HAP V4.2) was utilised to forecast the energy consumption of a Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB) at HCT, taking into account the availability of an Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV) and the absence of an ERV. The newly built house underwent a one-month testing phase to fulfil many duties according to competition regulations. One of the main goals was to generate on-site energy through photovoltaic panels, producing an amount proportional to the energy consumed by the house. Upon comparing the actual energy consumption data with the simulated result, it was noticed that the actual energy demand of the house was around 20% lower than the prediction made by the simulation tool.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1301
by Riadh Habash, Md Mahmud Hasan
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
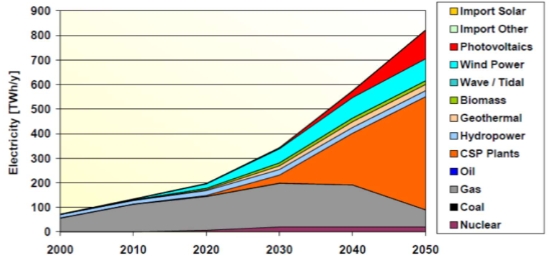
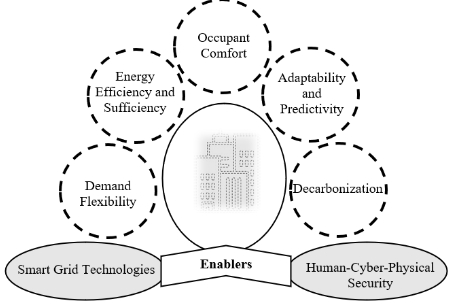
Today, grid-interactive, efficient buildings are gaining popularity due to their potential sustainability performances through their ability to learn, adapt, and evolve at different scales to improve the quality of life of their users while optimizing resource usage and service availability. This is realized through various practices such as management and control measures enabled by smart grid technologies, interoperability, and human-cyber-physical security. However, despite their great potential, the research of those technologies still faces various challenges. These include a lack of communication and control infrastructure to address interpretability, security, cost barriers, and difficulties balancing occupant needs with grid benefits. Initially, system modelling and simulation are promising approaches to address those challenges ahead of time. It involves consideration of complex systems made up of components from various research domains. This paper addresses the above practices, highlighting the value of integrating technology and intelligence in the planning and operation of buildings, both new and old. It provides a way to educate architects and engineers about this emerging field and demonstrates how these practices can help in creating efficient, resilient, and secure buildings that contribute to occupant comfort and decarbonization.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1334
by Yue Lyu
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
To study the variation of environment in the professional classroom during lecture hours, multiple field experiments and intervention experiments on indoor and outdoor temperatures were conducted in a university professional classroom in Shaoxing during the spring. Environmental data, including indoor and outdoor temperatures, relative, and CO2 concentrations, were recorded every 5 min. Volatile organic compounds (VOC) were sampled, and indoor air quality was evaluated repeatedly. Results showed that the classroom’s average indoor air temperature ranged from 17.8–29.2 ℃, the average indoor relative humidity from 34.5%–91.0%, the average CO2 concentrations from 921.6–1805.2 ppmv, and total VOC concentrations from 330–682 ppbm. The subjective evaluation conducted during the intervention experiments indicated a significant increase in perceived odor intensity upon entering the classroom. When the CO2 concentration reached 2000 ppmv, the satisfaction and acceptability of the air quality for the subjects and invitees decreased significantly. In the temperature range of 17–31 ℃, the CO2 emission rate of the human body was estimated to increase by 0.78 L/h for every 1 ℃ increase in temperature. To maintain the indoor CO2 concentration at 1000 ppmv, the required ventilation rate for each person must be increased by 0.25 ± 0.3 L/s.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1348
by Mushtaq Ahmed, Muhammad Azizul Hoque, H. M. A. Mahzuz, Nazmul Islam Rafi, Md. Jubayer Hossan Salman, Khadijatul Kubra Mim, Krisha Rana, Md. Abdullah Al Ahad, Md. Ariful Islam, Ratan Kumar Roy
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
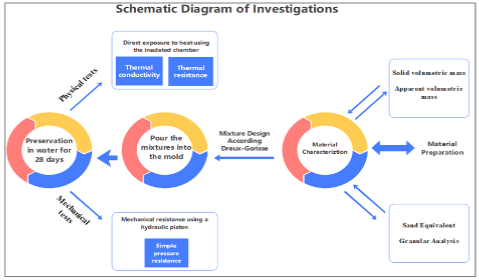
In this research, low-value plastic waste (LVPW) is used in concrete as a potential solution for sustainable waste management in the construction industry. In concrete, LVPW is utilized to produce Eco-Ring (Eco-conscious Latrine Ring). The use of a mix ratio of 1:2:3 and 1:2:4 in concrete mixes is studied. The impact of the percentage of recycled plastic on the mechanical properties of the final product is analyzed. The results show that the use of LVPW reduces both strength and unit weight but ensures its solidification. Sufficient strength for latrine rings is maintained, ensuring a balance between structural integrity and waste reduction. LVPW incorporation offers cost savings, with reductions of aggregate use up to 10%–15% in the present analysis. Justified consideration of the impact on mechanical properties, along with potential adjustments to optimize compatibility and address workability/aesthetics, can help maximize the benefits of this technology.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 544
by Yin Junjia, Aidi Hizami Alias, Nuzul Azam Haron, Nabilah Abu Bakar
Building Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
Machine learning, a key thruster of Construction 4.0, has seen exponential publication growth in the last ten years. Many studies have identified ML as the future, but few have critically examined the applications and limitations of various algorithms in construction management. Therefore, this article comprehensively reviewed the top 100 articles from 2018 to 2023 about ML algorithms applied in construction risk management, provided their strengths and limitations, and identified areas for improvement. The study found that integrating various data sources, including historical project data, environmental factors, and stakeholder information, has become a common trend in construction risk. However, the challenges associated with the need for extensive and high-quality datasets, models’ interpretability, and construction projects’ dynamic nature pose significant barriers. The recommendations presented in this paper can facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration between traditional construction and machine learning, thereby enhancing the development of specialized algorithms for real-world projects.