
Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
fmos
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 562
by K. Lilly Mary, D. Geetha, P.S. Ramesh
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.4, 2024;
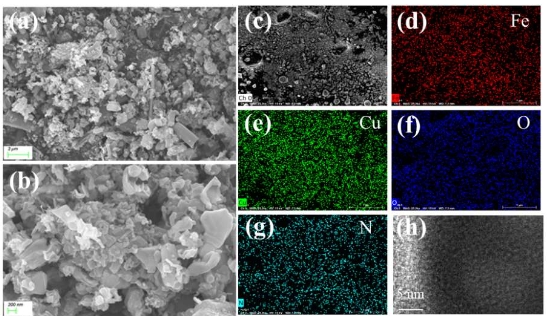
The unique copper-doped indium sulfide nanocrystals are synthesized by a gentle hydrothermal process. XRD, FTIR, XPS, FESEM/EDX, UV-DRS, and PL were used to characterize the final samples. Copper-doped indium sulfide nanostructures can be exploited as an active catalyst in photodegradation and as an electroactive material in supercapacitors due to their distinctive architecture. The copper-doped indium sulfide catalyst exhibits 85 percent photodegradation using methylene blue dye under natural sunlight irradiation, and the electrochemical test showed a capacitance of 668 Fg−1 at 1 Ag−1 in a 2 M KOH electrolyte solution. For future generations, photocatalyst and electrode can function as more desirable materials.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1815
by Makoto Shibahara, Yuuhi Hatta, Qiusheng Liu, Sutopo Purwono Fitri
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.4, 2024;
The effect of graphite powder on the thermal behavior of phase change material (PCM) was investigated experimentally. It is well known that the graphite is contributed to enhance the thermal response. However, the effect of graphite on the supercooling of the PCM is not clear when a highly heat conductive material is added. In this study, the specific heat of the PCM based on sugar alcohol such as D-mannitol and inositol was measured with an adiabatic scanning calorimeter. The enthalpy and entropy during the phase-change process were obtained by the measured specific heat of the PCM. Additionally, the exergy analysis was conducted to evaluate the thermal energy storage of PCM. As the experimental results, the specific heat of D-mannitol during the phase change process was higher than that of inositol. Moreover, it was found that the addition of graphite powder at the mass fraction of 9% improves the thermal behavior of D-mannitol with lower supercooling while maintaining latent heat. The suppression of supercooling by the addition of 9% graphite powder was 37.5%.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1546
by Grzegorz Augustyn, Jerzy Mikulik
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.4, 2024;
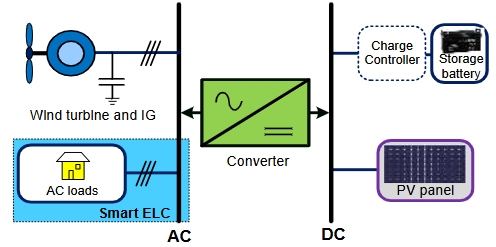
Energy management is nowadays key topic for synchronic operation of renewable sources of energy and their recipients. Contemporary national electrical power grid systems more often cannot supply efficiently electrical energy and cannot receive energy produced by renewable sources. The common approach to the problem is to meet energy demands supplying from electrical grid and renewable power sources with energy storage feature. From the other side, off-grid solutions based on the co-generation biogas plants are commonly aimed on small local communities as power supply supported by renewable energy systems like photovoltaic (PV) systems, wind power plants or small water plants with energy storage to support self-consumption of electrical energy. Integration of intermittent renewable power sources, such as solar, wind and biogas plant, increases the difficulty of managing the electricity grid and maintaining the balance of electricity supply and demand, especially in small communities. The holistic approach to the energy storage management takes all above aspects and presents the concept where municipal waste is used to produce energy in biogas plant supported by PV systems and community shared electrical energy storage to provide uninterrupted power supply. The study also presents how energy storage management can be used in whole process to adjust the size and manage energy supply and demand within the community based on energy self-consumption optimization. It is also shown that by utilizing municipal waste produced by the community we can meet the goals of circular economy and sustainable development of local communities as the waste will be used in full without necessity of recycling it outside the community. The novelty of the study is the foundation for energy storage capacity and renewable energy sources size evaluation to balance energy management process without the need of on-grid power supply and with use only municipal biodegradable waste for biogas fuel supply and solar energy for energy production.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 2074
by Surjit Sahoo, Anand Kumar Gandham, Vijay Kumar Pal
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.4, 2024;
Characterized by unique physical and chemical properties, metal oxide materials have garnered significant attention for research and development in energy storage device applications. In the current work, we present a simple and low-cost synthesis protocol for orthorhombic-phase niobium oxide (T-Nb2O5) electrodes, aimed at supercapacitor applications. The as-prepared T-Nb2O5 was characterized utilizing field emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, confirming the formation of orthorhombic-phase T-Nb2O5 nanoparticles. Detailed electrochemical analyses were conducted on T-Nb2O5, utilizing 1 M LiOH as the electrolyte. The unique nanoparticle architecture of T-Nb2O5 offers abundant electro-active sites and enhances reaction kinetics, leading to high specific capacitance. Notably, the T-Nb2O5 electrode achieved a gravimetric capacitance of approximately 23 F g−1 at the lowest sweep rate (5 mV s−1). These findings highlight the potential of T-Nb2O5 as an effective electroactive material for supercapacitors.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1631
by Lei Li, Fanmin Kong, Ang Xiao, Hao Su, Xiaolian Wu, Ziling Zhang, Haoqi Wang, Yutian Duan
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.4, 2024;
Owing to the escalating demand for environmentally friendly commodities, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are gaining extensive recognition as a viable means of energy storage and conversion. LIBs comprise cathode and anode electrodes, electrolytes, and separators. Notably, the separator, a crucial and indispensable element in LIBs that mainly comprises a porous membrane material, necessitates substantial research focus. Scholars have consequently strived to devise novel systems that augment separator efficiency, bolster safety measures, and surmount existing constraints. This review endeavors to equip researchers with comprehensive information on polyolefin-based separator membranes, encompassing performance prerequisites, functional attributes, scientific advancements, and so on. Specifically, it scrutinizes the latest innovations in porous membrane configuration, fabrication, and enhancement that utilize the most prevalent polyolefin materials today. Consequently, robust and enduring membranes fabricated have demonstrated superior effectiveness across diverse applications, facilitating a circular economy that curbs waste materials, reduces operational expenses, and mitigates environmental impact.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1613
by Ruby Garg, Mohit Agarwal
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.4, 2024;
MXenes have imposed a profound effect on materials science and nanotechnology fields after their discovery in 2011. Theoretical models have predicted more than 100 potential compositions of MXene whereas laboratory-scale synthesis reflects their success of over 40 distinct structures till date. The distinctive properties of MXenes have led to their use for a diverse range of applications, such as energy storage, environmental remediation, electronics, communications, gas and liquid separation and adsorption, biomedical fields, and optoelectronics. The increased interest of researchers in MXenes has led to a wide rise in research publications, showing their growing importance in different scientific domains. In 2024, MXenes had shown wide potential in various areas, including energy storage devices, electromagnetic interference shielding, nanocomposites, and hybrid materials. However, the variations in the choice of precursors, reactor design, cost, synthesis parameters pose several challenges in ensuring the production of high-quality MXenes. The applicability of MXenes continues to broaden as its compositions are continuously accelerating. This review aims is to provide a comprehensive overview of MXene history, its properties, challenges, latest trends, and different applications to highlight its potential and gather new audiences towards this family of two-dimensional materials.