
Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
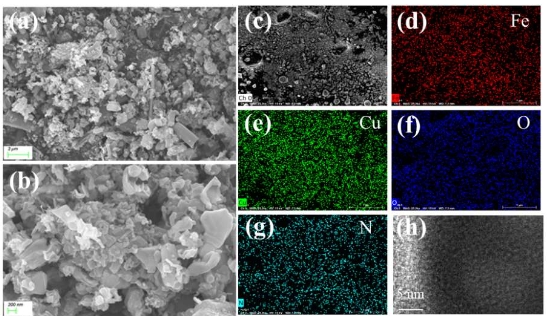
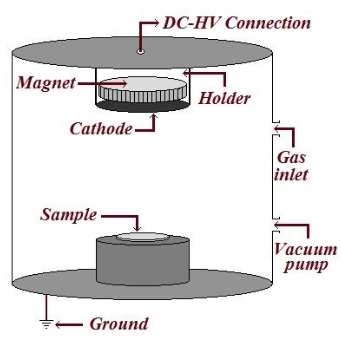
fmos
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 2211
by George Efthimiou
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
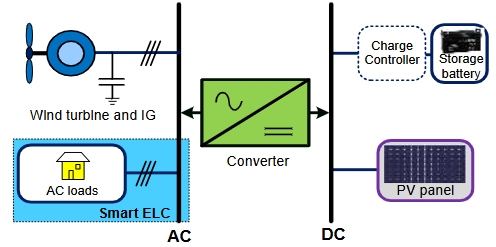
This study investigates the maximum wind energy potential of points that exhibit the highest correlation in an urban environment. A wind tunnel experiment that was simulated in a previous study using the Large Eddy Simulation (LES) methodology to generate wind speed time series at various locations within a complex urban setting. The analysis focuses on the correlation of wind speeds at different heights and spatial points, demonstrating a clear dependence on height, with maximum correlations generally increasing as height increases. This phenomenon is attributed to the disruption of turbulent eddies by buildings, which significantly influences the wind flow patterns. The Spectral Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (SPOD) technique is employed to calculate the maximum wind energy, revealing that the maximum values occur on building rooftops. Additionally, an empirical equation is proposed, relating the maximum wind energy to the distance between the most correlated points, with a relatively high correlation coefficient. The findings of this research have practical implications for the optimization of renewable energy resources, particularly in urban environments where wind flow is highly complex. This study contributes to the understanding of wind energy potential in urban settings, offering insights that could be valuable for the placement and design of wind turbines in such challenging environments. The study revealed a significant dependence of wind energy potential on spatial positioning and height, with maximum values occurring at rooftops. An empirical equation was developed to predict the difference in maximum wind energy based on the distance between highly correlated points, offering a practical tool for urban wind energy optimization. These findings provide actionable insights for the integration of renewable energy systems in complex urban settings.
 Open Access
Open Access
Perspective
Article ID: 2515
by Ayesha Kausar
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
In light of eras of scientific endeavors on carbon nanotubes and related nanomaterials, we notice extending applications of carbon nanotubes from high-tech energy/electronic devices to defense, engineering, and medical fields. Carbon nanotubes, being one of the initial nanocarbon technology breakthroughs, emerged as a frontline competitor for designing advanced energy devices/systems. As per literature so far, carbon nanotubes render valuably high specific surface area/properties, design adaptabilities, structural synergies, low expenses/density/toxicity, interfacial/percolation effects, and desirable energy storage (charge/electron flow, capacity/capacitance, capacity retention, reversible discharge, cyclic span, etc.) and energy conversion (power conversion efficiencies, energy/power density, photovoltaic effects, durability, etc.) parameters for devices. Looking at the up-to-date demand for carbon nanotubes in high-end energy storage and conversion systems (batteries, capacitors, photovoltaics), this perspective manuscript is planned to unveil the actual state-of-the-art and advancements in this field. Despite the success to date, real-world employment of carbon nanotube-derived energy systems seems to rely upon overcoming challenges for integrating these nanomaterials in next-generation energy assemblies. To meet current technological necessities, green-sourced carbon nanotube nanomaterials must be practiced for modern and future sustainable energy industries.