
Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
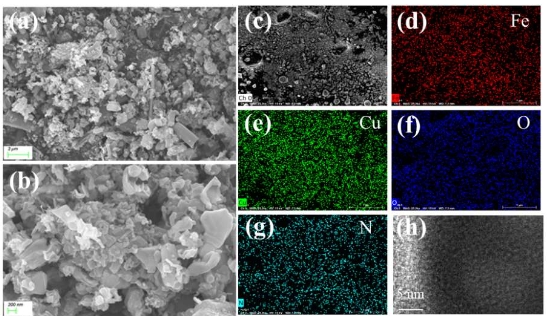
fmos
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 426
by Youssef El Haj, Vijay Sood, Ahmed Sheir, Ruth Milman
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
This work proposes a systematic approach to designing a novel integral sliding mode controller (ISMC) for a single-ended primary-inductor converter (SEPIC) with only one tunable parameter where the upper and lower bounds are derived. The designed surface results in minimal chattering behaviour at the output voltage as well as at the duty cycle and allows for operating the SEPIC at a fixed switching frequency. The proposed controller can withstand up to a 70% variation in the input voltage and 100% variation on the load side, in addition to superior performance for a cold start. The proposed controller and the corresponding mathematical formulation were simulated in a Simulink environment and experimentally tested via a scaled prototype. The proposed controller performance is also compared to Type II and integral Linear-Quadratic Regulators (LQR).
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 214
by Muhammed Fatih Saltuk
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
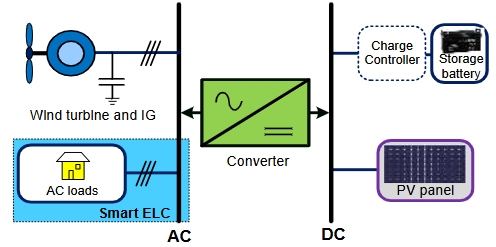
Hybrid facility investments from renewable energy sources have increased in recent years. In general, solar power is the secondary energy source in hybrid systems. The reason why solar energy is most commonly used in hybrid power systems is that it is cheaper than other types of renewable energy. Solar-Hydroelectric (SHE) is one of the foremost compatible hybrid energy pairs, as solar and hydroelectric power generation profiles complement one another. Hybrid systems consisting of solar and hydropower have complementary characteristics due to the shared use of infrastructure systems and different periodicities in power generation. Energy management is important for SHE-integrated facilities. Since only a limited amount of energy can be injected into the grid from transformer capacities, energy management in hybrid systems is of great importance. To manage energy in hybrid energy systems, the amount of energy that can be produced each hour must be determined. In hybrid energy plants, there is usually already another renewable energy plant in place, and solar energy is added on top and optimized. Since there are no pyrometers in the existing plants, the daily radiation data from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is used, but the daily energy production amount may be insufficient for accurate energy management. To realize this, it’s necessary to reveal the energy generation on an hourly basis. During this study, the quantity of radiation on an hourly basis was determined to calculate solar power generation. Empirical and econometric models utilized in radiation amount determination were performed, and the most appropriate method was clarified by comparing them with one another. Hourly-based radiation is achieved with an empirical method by using National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) daily radiation.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 457
by Jyoti Bhattacharjee, Subhasis Roy
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
The need for clean and renewable energy has grown dramatically over the past few years. As potential candidates for producing green energy in this region, photovoltaic and bio-solar energy technologies have arisen. This review presents a novel approach for designing and developing photovoltaics and bio-solar cells using eco-friendly materials and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques. An intriguing architecture is outlined for a bio-solar cell that fuses photovoltaic electronics with photosynthetic organisms. A recyclable thin-film solar cell serves as the basis of our photovoltaic system. To further maximize the effectiveness of the device, we use AI algorithms. According to statistical calculations, the proposed bio-solar cell can produce a sizable amount of electricity while being ecologically sound. This paper outlines significant advances in developing solar cells and photovoltaics using green nanomaterials and AI, which provide exciting potential for improving energy harvesting capacity. This review also presents an overview of the effects of the potential commercialization of our strategy, its social and environmental benefits, and its pitfalls.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 491
by Yuping Wu, Rudolf Holze
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
Similarities and analogies between materials, structures, operating and construction principles of secondary batteries and supercapacitors and their electrodes are presented, named, and reviewed in context. On the material level, several materials used both in batteries and supercapacitors are addressed, and implications from observations made in one application for the other are highlighted. On the electrode level, a continuous change of architectural details is observed when going from an electrode with high charge storage capability to an electrode supporting high currents is detected; again, this overlap provides instructive ideas for both fields. On the cell level, combinations of electrodes from both fields yielding hybrid devices are an obvious outcome again, with implications for both fields. Ideas and suggestions for further research and development based on a deeper exchange between both families are developed.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 436
by Kerim Karabacak
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
The integration of supercapacitors in photovoltaic (PV) energy systems holds immense potential for enhancing energy storage, reliability, and efficiency. This article provides a comprehensive overview of recent advancements, challenges, and opportunities in the utilization of supercapacitors within PV systems. Fundamental principles of supercapacitor operation, including charge storage mechanisms and electrode materials, are discussed, highlighting their unique advantages such as high power density and rapid charge/discharge capabilities. Various integration strategies, including parallel and series configurations, as well as system-level control algorithms, are examined to optimize energy management and performance. Case studies and real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of integrated PV and supercapacitor systems across different applications and scales. According to the results of the research, 235 publications have been made on the subject in the last fifteen years, and the number of publications has doubled in the last five years. Additionally, future research directions focus on improving energy density, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, as well as addressing challenges related to temperature sensitivity and system scalability. Overall, the integration of supercapacitors in PV systems offers promising solutions for advancing sustainable energy solutions and accelerating the transition towards a cleaner, greener future.