
Xi'an Jiaotong University, China
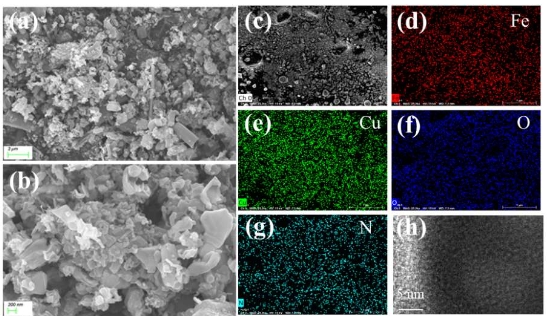
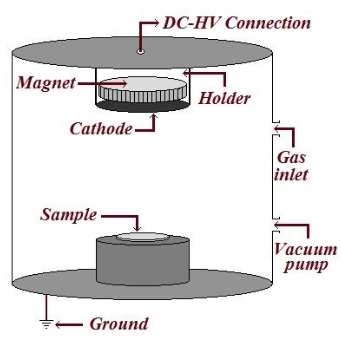
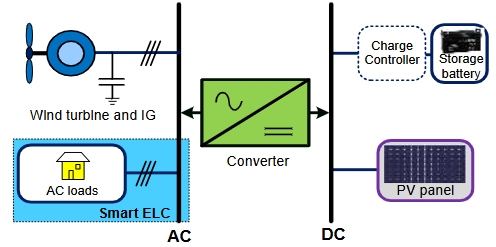
fmos
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1764
by Miłosz Ciurkot, Piotr Olczak
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
In the face of European climate policy, the aim of which is to achieve climate neutrality by 2050, we are still looking for alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. Apart from the obvious solutions offered by wind and solar energy, it is worth paying attention to a still undeveloped, but potentially developing branch of energy, which is generating energy from biogas. Poland currently produces 638 million m3 of biogas per year and has biogas installations with a total installed capacity of 276 MW. However, these numbers still do not fully satisfy both Polish possibilities and needs. This study analyzes the current use of this fuel in the Polish energy sector, as well as the possibilities and future prospects for biogas as a fuel for distributed generation power plants in Poland. The current review of the use of biogas as a fuel clearly indicates that biogas is not a commonly used renewable energy source with a total share of power among other RES sources of 4.2%. The analyses also indicated that the maximum theoretical Polish potential for biogas production may reach even 4.2 billion m3. At the end of the article, simple financial analyses were made regarding the profitability of investments in agricultural biogas plants, and their results showed a high profitability of investments in such energy units (theoretical payback periods of financial outlays are only 4 years).
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1957
by Aasim A. Azooz, Zeyad T. Ali
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
A quantitative model-based analysis was conducted to estimate the percentage output energy ratio of vertically installed bifacial PV modules in fences, cattle barriers, and roadsides compared to the output energy of two types of monofacial PV installations. The first comparison is between the output of the vertical bifacial PV fence and the output of the same fence furnished with vertically installed monofacial PV modules. The second comparison is between the output of the vertical bifacial fence and the output of south-facing monofacial PV modules installed at the optimal inclination angle for the particular latitude. The results show that bifacial fences can produce net yearly energy outputs up to 80% higher than those of monofacial PV modules. Additionally, vertical bifacial PV fences produce only a few percent lower energy compared to optimally installed monofacial PV modules. A MATLAB software program was written to calculate the gain of fences of any geometry, and it has been made freely available. Examples of gain results for a few such geometries are presented.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1956
by Shifeng Wang, Sicong Wang
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
The enhanced wake turbulence generated by wind turbine has remarkable effects on the power generation and fatigue loads of wind farm and the environment. The paper investigates the mechanism of the impacts of the wind turbine characteristics on the wake turbulence, to provide new knowledge on the design of wind turbine to wind turbine manufacturing factories. A novel wake turbulence coefficient is developed to quantify the ratio of the generated turbulence kinetic energy to the captured wind energy, and is derived as the function of wind turbine characteristics. This wake turbulence coefficient model is explored under optimal conditions. Results show that the wake turbulence coefficient decreases sharply with the increasing power coefficient of wind turbine. The larger the power coefficient is, the smaller the decrease of wake turbulence coefficient. Therefore, it is an effective way to reduce the enhanced wake turbulence through increasing the power coefficient, especially when the power coefficient is small. The wake turbulence intensity is the strongest around the hub of rotor and the weakest around the tip of rotor. It is therefore important to design the structure of the hub of rotor to reduce the enhanced wake turbulence.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1984
by Cihan Yalçın
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
The present study assesses the influence of thermal imaging defect detection on the energy efficiency of a 1.6 MW solar power facility in the Bağyurdu Organized Industrial Zone (OIZ) in İzmir, Turkey. Thermal imaging has demonstrated efficacy in detecting serious problems in photovoltaic (PV) panels, including hot spots, inoperative modules, faulty connections, and shadowing, which substantially impact system performance. A comprehensive investigation revealed that around 15% of the photovoltaic panels displayed defects, resulting in a 16% decrease in system performance and an estimated yearly energy loss of 0.35 GWh. The study emphasizes the benefits of thermal imaging compared to conventional fault detection techniques, including its capacity for swift and non-invasive identification of localized overheating, which may lead to fires, and its ability to discern fluctuations in energy output due to shading or malfunctioning modules. The results underscore the necessity for routine thermal evaluations and maintenance to guarantee photovoltaic systems’ operational efficacy and dependability. This study enhances the sparse data on large-scale photovoltaic systems in Türkiye and illustrates the effectiveness of thermal imaging as an economical and accurate diagnostic instrument. Future studies should amalgamate thermal imaging with sophisticated diagnostic techniques, like electroluminescence testing and machine learning, to augment fault detection precision and optimize photovoltaic system efficacy.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 2181
by Bahar Panbechi, Ali Roghani Araghi
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
This article presents a detailed assessment of the economic feasibility of establishing a forest biomass power plant using a mathematical programming model that incorporates various operational and economic factors. Results indicate that this power plant is currently unprofitable, highlighting the financial challenges renewable energy projects face. Multiple factors, such as transportation costs, CO2 penalties, and local employment impacts, significantly affect the net revenue generated from electricity derived from wood products. The need for strategic interventions to improve revenue generation and enhance the profitability of forest biomass power plants is evident. In this article, in addition to examining the challenges, suggestions will be provided to improve the economic status of biomass power plants, which can assist stakeholders in their future decision-making.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1920
by Ruby Garg
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
MXenes belongs to a family of two‐dimensional (2D) layered transition metal carbides or nitrides which shows outstanding potential for various energy storage applications because of their high‐specific surface area, phenomenal electrical conductivity, outstanding hydrophilicity, and variable terminations. Of these different types of MXenes, the most widely studied member is Ti3C2Tx especially in supercapacitors (SCs). However, due to the problem of stacking and oxidation in MXene sheets, significant loss of electrochemically active sites happens. To overcome these issues, incorporation of carbon materials is carried out into MXenes for enhancing its electrochemical performance. This review aims to introduce various common strategies employed in synthesizing Ti3C2Tx, followed by a brief overview of latest developments in fabricating Ti3C2Tx/carbon electrode materials for SCs. The composition of Ti3C2Tx/carbon are summarized based on different dimensions of carbons, such as 0D carbon dots, 1D carbon nanotubes and fibers, 2D graphene, and 3D carbon materials (activated carbon, polymer‐derived carbon, etc.). Further, this review also aims in highlighting several insights on fabrication of novel MXenes/carbon composites as electrodes for application in SCs.
 Open Access
Open Access
Perspective
Article ID: 1959
by Christopher Ian Wright
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
This article discusses typical heat transfer fluids (HTFs), crucial for efficient heat transfer in various industrial processes. HTFs play an important role circulating heat within closed-system operations, such as chemical processing, and also in storing and transferring thermal energy, for example, in concentrated solar power plants. Selecting the right HTF is key, as it must be compatible with the specific temperature range of the operation, thermally stable at high temperatures, and compatible with system materials. Safety is also a crucial factor, both in terms of personal safety during handling of the fluid and environmental impact of fluids. Regular monitoring is also a key consideration when selecting and using a fluid. as the condition of the HTF and system are interlinked. Regular sampling and monitoring of the fluid’s condition helps to identify potential issues like oxidation, contamination, and thermal decomposition, and thus helps to prevent or slow degradation while sustaining optimal performance. Strategies for extending the lifespan of a HTF include routine monitoring and the utilisation of other technologies, as needed, to protect against oxidation (e.g., anti-oxidative additive packages) and volatile light-ends (e.g., installation of a light-ends removal kit). By adopting such measures, industries can reduce operating costs, minimize downtime, and improve overall system efficiency. The objective of this short review is to provide a brief overview of the main HTFs used in high temperature industries and offer insights into the importance of selecting the right HTF for a specific application, considering factors such as its thermal properties, chemical stability, and safety. The need for regular monitoring and maintenance is emphasized to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of HTFs.
 Open Access
Open Access
Perspective
Article ID: 2198
by Ayesha Kausar
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.1, 2025;
Nowadays, mainstream research on graphene trends towards employing environmentally friendly or green synthesis routes and precursors, and ensuing green graphene nanomaterials are shown to be highly beneficial for a range of scientific applications, from energy/electronics to engineering to biomedical arenas. Specifically, graphene has emerged as a leading contender for designing green or ecological energy conversion (solar cells, fuel cells) and energy storage (supercapacitors, batteries) devices/systems. In this perspective article, we basically aim to highlight state-of-the-art advancements of green-sourced graphene and related nanomaterials in today’s energy sectors. According to scientific endeavors so far on green graphene, its successful design, real-world energy conversion/storage device application, and commercialization depend upon resolving underlying challenges of synthesis/performance. We observe notable applications of green graphene in the fields of photovoltaics, fuel cells, capacitors, and batteries. Herein, we suggest comprehensive future surveys for advanced fabrication techniques and sustainable sources/techniques to develop next-generation green graphene-derived energy systems with superior energy storage capacities and power outputs.