Graphene going green—Today’s energy scenarios
Abstract
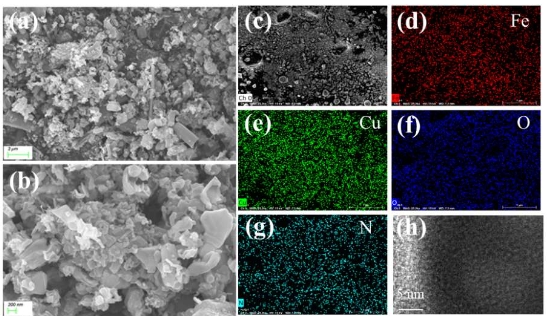
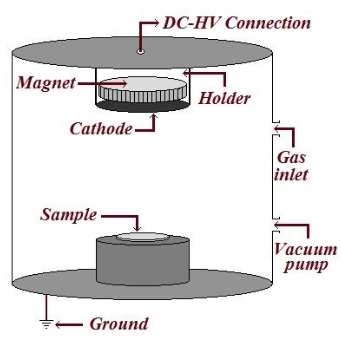
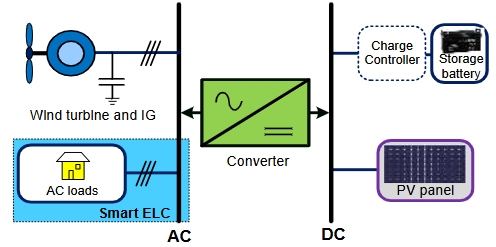
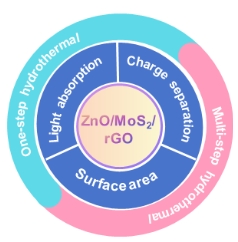
Nowadays, mainstream research on graphene trends towards employing environmentally friendly or green synthesis routes and precursors, and ensuing green graphene nanomaterials are shown to be highly beneficial for a range of scientific applications, from energy/electronics to engineering to biomedical arenas. Specifically, graphene has emerged as a leading contender for designing green or ecological energy conversion (solar cells, fuel cells) and energy storage (supercapacitors, batteries) devices/systems. In this perspective article, we basically aim to highlight state-of-the-art advancements of green-sourced graphene and related nanomaterials in today’s energy sectors. According to scientific endeavors so far on green graphene, its successful design, real-world energy conversion/storage device application, and commercialization depend upon resolving underlying challenges of synthesis/performance. We observe notable applications of green graphene in the fields of photovoltaics, fuel cells, capacitors, and batteries. Herein, we suggest comprehensive future surveys for advanced fabrication techniques and sustainable sources/techniques to develop next-generation green graphene-derived energy systems with superior energy storage capacities and power outputs.
References
[1]Santra S, Bose A, Mitra K, et al. Exploring two decades of graphene: The jack of all trades. Applied Materials Today. 2024; 36: 102066.
[2]Kausar A. Graphene to Polymer/Graphene Nanocomposites: Emerging Research and Opportunities. Elsevier; 2021.
[3]Khan S, Ullah I, Khan S, et al. Advancements in nanohybrids: From coordination materials to flexible solar cells. Journal of Polymer Science and Engineering. 2024; 7(1): 4276.
[4]Tiwari S, Mohammed KS. Unraveling the impacts of linear economy, circular economy, green energy and green patents on environmental sustainability: Empirical evidence from OECD countries. Gondwana Research. 2024; 135: 75–88.
[5]Huang L, Gan Y. A review on SEM imaging of graphene layers. Micron. 2024; 103716.
[6]Geim AK, Novoselov KS. The rise of graphene. Nature materials. 2007; 6(3): 183–191.
[7]Lu Z, Han T, Yao Y, et al. Fractional quantum anomalous Hall effect in multilayer graphene. Nature. 2024; 626: 759–764.
[8]Zafar M, Imran SM, Iqbal I, et al. Graphene-based polymer nanocomposites for energy applications: Recent advancements and future prospects. Results in Physics. 2024; 107655.
[9]Leng X, Vazquez RJ, McCuskey SR, et al. Bacteria-loaded graphene bioanode for renewable energy generation. Carbon. 2023.
[10]Torres FG, Troncoso OP, Rodriguez L, et al. Sustainable synthesis, reduction and applications of graphene obtained from renewable resources. Sustainable Materials and Technologies. 2021; 29: e00310.
[11]Soni J, Teli P, Agarwal S. Recent Advances in the Green Reduction of Graphene Oxide and its Potential Applications. Current Nanoscience. 2024; 20(2): 146–156.
[12]Jo SG, Ramkumar R, Lee JW. Recent Advances in Laser‐Induced Graphene‐Based Materials for Energy Storage and Conversion. ChemSusChem. 2024; 17(5): e202301146.
[13]Alabi AS, Popoola AP, Popoola O, et al. Materials for electrocatalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cell: A brief review. Frontiers in Energy Research. 2023; 11: 112.
[14]Muzaffar A, Ahamed MB, Hussain CM. Green supercapacitors: Latest developments and perspectives in the pursuit of sustainability. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2024; 195: 114324.
[15]Xia Z, Li Z, Xu J, et al. Green synthesis of positive electrodes for high performance structural batteries-A study on graphene additives. Composites Science and Technology. 2024; 251: 110568.
[16]Cassee FR, Bleeker EA, Durand C, et al. Roadmap towards safe and sustainable advanced and innovative materials. (Outlook for 2024–2030). Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. 2024; 25: 105–126.
[17]Jia C, Pang M, Lu Y, et al. Graphene environmental footprint greatly reduced when derived from biomass waste via flash Joule heating. One Earth. 2022; 5(12): 1394–1403.
Copyright (c) 2025 Author(s)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.