Story of carbon nanotube in energy—Booms and lapses?
by Ayesha Kausar
Energy Storage and Conversion, Vol.3, No.2, 2025;
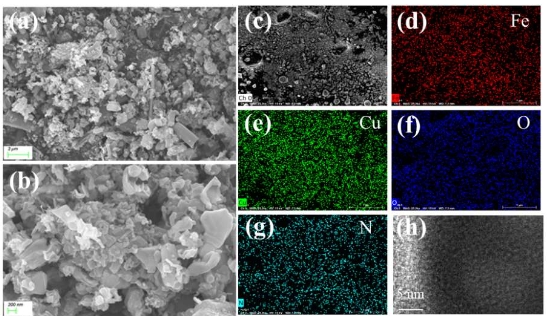
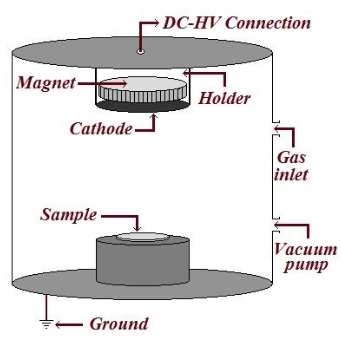
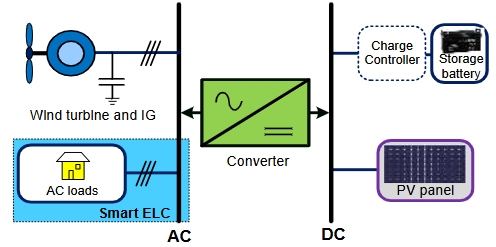
In light of eras of scientific endeavors on carbon nanotubes and related nanomaterials, we notice extending applications of carbon nanotubes from high-tech energy/electronic devices to defense, engineering, and medical fields. Carbon nanotubes, being one of the initial nanocarbon technology breakthroughs, emerged as a frontline competitor for designing advanced energy devices/systems. As per literature so far, carbon nanotubes render valuably high specific surface area/properties, design adaptabilities, structural synergies, low expenses/density/toxicity, interfacial/percolation effects, and desirable energy storage (charge/electron flow, capacity/capacitance, capacity retention, reversible discharge, cyclic span, etc.) and energy conversion (power conversion efficiencies, energy/power density, photovoltaic effects, durability, etc.) parameters for devices. Looking at the up-to-date demand for carbon nanotubes in high-end energy storage and conversion systems (batteries, capacitors, photovoltaics), this perspective manuscript is planned to unveil the actual state-of-the-art and advancements in this field. Despite the success to date, real-world employment of carbon nanotube-derived energy systems seems to rely upon overcoming challenges for integrating these nanomaterials in next-generation energy assemblies. To meet current technological necessities, green-sourced carbon nanotube nanomaterials must be practiced for modern and future sustainable energy industries.
show more





 Open Access
Open Access