

 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1379
by Milad Shahvaroughi Farahani, Ghazal Ghasmi
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
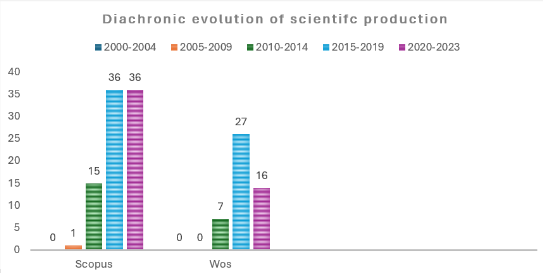
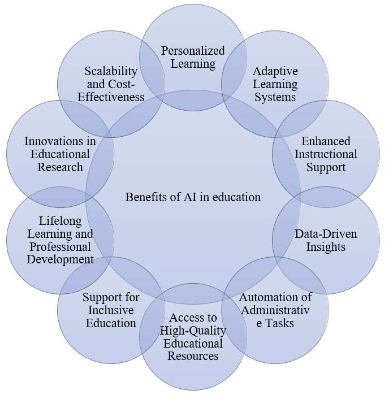
This comprehensive study delves into the multifaceted role of AI in education, exploring its applications, benefits, challenges, and future implications. The purpose of the study is to show how AI in education helps educators identify gaps in student knowledge and provide targeted feedback to improve learning outcomes. As a methodology, the library method and the study and review of various documents have been used in this research. The study examines the diverse range of AI technologies employed in educational settings, including intelligent tutoring systems, personalized learning platforms, educational chatbots, and virtual reality simulations. Furthermore, the study delves into the numerous benefits that AI brings to education. It highlights how AI-powered analytics and data-driven insights enable educators to gain deeper insights into student learning patterns, identify areas for improvement, and tailor instructional strategies accordingly. Additionally, AI-driven tools promote inclusivity by providing personalized support to learners with diverse needs and learning styles. Despite its transformative potential, the study also acknowledges the challenges and ethical considerations associated with integrating AI into education. Data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the digital divide are examined in detail, emphasizing the importance of responsible AI deployment and ethical guidelines. Looking ahead, the study explores the future implications of AI in education and the evolving role of educators in AI-enabled classrooms. It discusses how AI technologies will continue to evolve, offering new opportunities for collaborative learning, skill development, and lifelong education. In conclusion, this comprehensive study underscores the profound impact of AI on education and the need for thoughtful implementation strategies that prioritize equity, inclusivity, and ethical considerations. By harnessing the potential of AI, education systems can better prepare learners for the challenges and opportunities of the future.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1507
by Federico Valente
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
The purpose of this paper is to investigate whether CLIL (Content and Language Integrated Learning) can lead Italian high school students to improve their English as a Foreign Language speaking skills. The trigger for this research comes from my EFL teaching experiences at Italian schools, where the syllabi employed tend to neglect the training of speaking skills and focus mainly on grammar translation and English literature instructions. The stimulus for this investigation comes also from articles on the effectiveness of using CLIL for the improvement of FL speaking performance and Lexis extension that I read before writing this article in order to have a broader view of this topic. The literature review describes in detail theoretical issues with regard to the advantages of using CLIL methodology in the classroom over traditional approaches and how this technique helps FL students to facilitate speaking difficulties. It also makes reference to a few key findings from previous research. This study was conducted in Italy, and the data gathering processes consist mainly of qualitative, semi-structured interviews with five participants (three EFL learners and two experienced teachers of English as a foreign language), interview transcripts, and content analysis techniques that I used to examine and interpret the collected data. Findings indicate that not only can content and language integrated learning represent an improvement of the common EFL teaching methods and help learners enhance their speaking abilities, but it can also stimulate their motivation to study English and lower learners’ levels of anxiety, which is commonly associated with their concern about making mistakes or being assessed.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1513
by Hammad Hussain Shah, Sumera Iqbal, Khizar Abbas, Ushba Rasool
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
This article employs narrative discourse analysis to analyze James Joyce’s short story “Araby” by using two narrative analysis frameworks that focus on the macrostructure and microstructure aspects of the story. The analysis covers the story’s purpose, generic structure, and lexico-grammatical cohesion. The writer follows a series of structural moves and uses a variety of narrative strategies (e.g., a high level of involvement and a wide range of lexical and grammatical cohesive ties), which contribute to the creation of a well-formed text that has effectively achieved its purpose and made its intended effect. This macro-structural analysis sheds light on the story’s thematic elements, character development, and overall narrative trajectory, providing a deeper understanding of its intended message and impact. The article unveils Joyce’s underlying linguistic mechanisms to convey meaning and evoke emotion within the narrative. By exploring the story’s purpose, structure, and linguistic nuances, the analysis offers valuable insights into Joyce’s narrative techniques and the profound impact of “Araby” as a well-formed literary text. This analysis of James Joyce’s “Araby” through narrative discourse analysis offers valuable insights that can be applied in the classroom to enrich student engagement with literature.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1415
by Emily Barnes, James Hutson, Karriem Perry
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
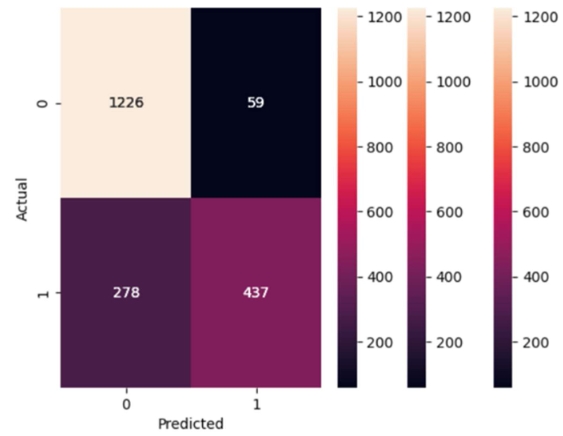
This article explores the use of machine learning, specifically Classification and Regression Trees (CART), to address the unique challenges faced by adult learners in higher education. These learners confront socio-cultural, economic, and institutional hurdles, such as stereotypes, financial constraints, and systemic inefficiencies. The study utilizes decision tree models to evaluate their effectiveness in predicting graduation outcomes, which helps in formulating tailored educational strategies. The research analyzed a comprehensive dataset spanning the academic years 2013–2014 to 2021–2022, evaluating the predictive accuracy of CART models using precision, recall, and F1 score. Findings indicate that attendance, age, and Pell Grant eligibility are key predictors of academic success, demonstrating the strong capability of the model across various educational metrics. This highlights the potential of machine learning (ML) to improve data-driven decision-making in educational settings. The results affirm the effectiveness of Decision Tree (DT) models in meeting the educational needs of adult learners and underscore the need for institutions to adapt their strategies to provide more inclusive and supportive environments. This study advocates for a shift towards nuanced, data-driven approaches in higher education, emphasizing the development of strategies that address the distinct challenges of adult learners, aiming to enhance inclusivity and support within the sector.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1394
by Abreha Tesfay Weldeslassie, Tesfay Haile
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
Content analysis is a research tool used to determine the presence of certain words, themes, or concepts within, for example, textbooks. Mathematics textbooks have a significant impact on students’ learning due to their role during the instructional processes. Both quantitative and qualitative data from primary and secondary sources were employed using content analysis of grade-12 mathematics textbooks and responses from 23 teachers from schools in three randomly selected zones out of seven. The objective is to identify strengths and/or weaknesses of the textbook and challenges affecting teachers’ instructional practices, thereby recommending corrective measures to be taken by stakeholders and policymakers. The nine units/sub-topics of the textbook have been analyzed in terms of coverage, vertical-horizontal relationships, integration, continuity, sequence, and the application of higher-level cognitive objectives. Results from responses to closed-and open-ended questions revealed that major problems with the instructional practices include low interest of students (Mean = 4.22, SD = 1.06) resulting in a high rate of migration, bulky content (Mean = 4.0, SD = 1.14), lack of support from parents (Mean = 3.78, SD = 0.98), shortage of time/period allotment (Mean = 3.65, SD = 1.05), and insufficient training (Mean = 3.35, SD = 1.05). The identified themes/patterns are narrated, sequenced, and interpreted using different perspectives. Findings indicated that there are no conceptual problems throughout, but there are weaknesses in the textbook, such as the problem of horizontal articulation with other subjects like physics. There is a need to address the imbalance on the cognitive objectives, and teachers focus on lecturing to cover the voluminous content. This requires due attention through the participatory approach model (PAM), including awareness creation to reduce migration and providing continuous short-term trainings for teachers as per set national and/or international standards at all levels to improve the quality of education.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1430
by Kamal Prasad Koirala, Krishna Prasad Parajuli
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
This article explores the integration of STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) education into the secondary school science curriculum. It provides an in-depth analysis of the current state of STEAM education, challenges, successes, and future directions. The article draws on literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and interviews with science teachers to offer a holistic view of the benefits of STEAM education integration at school-level science teaching. This study was carried out by selecting three schools in the Gorkha district and three science teachers who are implementing separate types of STEAM-based project approaches in science teaching. This study found that science teachers attempted to implement the project-based technology-friendly STEAM approach in their classrooms. However, they faced several obstacles to the integration of STEAM into the present school science curriculum due to the limited availability of internet facilities. It suggests that policy level and curriculum designers prepare the STEAM-based curricula for transdisciplinary (STEAM-based) school science teaching.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1418
by Ignatova Darinka, Dimitrova Bistra, Iliev Alexander, Angelova Petya
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
This article aims to establish trends in motor development through basketball activities as a prerequisite for building a wellness culture, revealing the impact of basketball exercises on motor activity in junior high school. The interests of the research are aimed at following the dynamics in the motor potential and establishing and evaluating the presence of wellness within the framework of school physical education. More specifically, the creation of a culture of wellness in the junior high school stage of the educational degree. A reliable and objective toolkit for diagnosing the level of motor potential in 12–14-year-old students was selected and applied, specifying the empirical data from the conducted research. The purpose of the research is to follow the dynamics of the motor potential in the two stages of research and to establish a wellness culture in the junior high school stage of the educational degree in the lesson of physical education and sports, based on a comparative analysis of the dynamics of motor indicators in the two cognitive stages of the study. Through legislative changes in school education, the direction “school health”, in particular the expected competences, is regulated. Key competence #9 requires knowledge and skills for sustainable development, implementation of a healthy lifestyle, and sports in the Bulgarian school. To achieve the goal, the following research tasks are solved: experimentation of a basketball training program aimed at the development of motor qualities, as a result of which the dynamics in the development of motor qualities of students studying basketball in physical education and sports classes. Based on the benchmarking analysis, it can be concluded that the results achieved at baseline show an improvement in the motor condition of the studied contingent. Motor indicators show intense dynamics in 12–14-year-old students, modeling their motor potential and confirming the presence of a wellness culture in the Bulgarian school. It can be summarized that a benchmarking analysis was carried out to establish dynamics in the indicators and the manifestation of motor skills between the students of the 4th and 5th grade, allowing the individualization of the differences in the motor potential between the empirical data in the cognitive stages of the study.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 279
by Yurii Tulashvili
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
The new concept of humanizing society, founded on the priority of personality development through socialization processes, opens new perspectives for citizens with visual impairments in Ukrainian society. The article analyzes the issue of social adaptation of this category of people through inclusive education, which encompasses preschool, general, and vocational training. The historical, philosophical, psychological, and methodological aspects of implementing an integrative approach to inclusive education for visually impaired individuals are considered. The study emphasizes the importance of the “principle of equal opportunities” in education for children and youth with functional limitations, focusing on the integration of such individuals into the general educational process. It underscores the need for a societal attitude shift towards children with special educational needs and the support for the idea of inclusion at the state level, involving school administrators, educational staff, parents, and other participants in the educational process. The psychological and pedagogical support of children with visual impairments within the context of inclusive education, playing a key role in the development of Ukraine’s modern educational system, is distinguished by its multidisciplinary approach. This support ensures the preparation and psychological readiness of all participants in the educational process for cooperation with children with health issues and includes the prevention and correction of secondary developmental deviations in such children. Special attention is paid to the role of social and pedagogical work in the development of a child with disabilities in accordance with the general patterns of child development, considering secondary symptoms related to abnormal social development. The article investigates the main approaches to implementing inclusive education in the educational space of Ukraine. The author examines the normative legal acts concerning the integration of people with special needs and their impact on the development of democracy. Additionally, an overview of the experience of organizing education for people with visual impairments in Ukraine and abroad is provided. The authors of the article highlight the need for support of regional rehabilitation and social protection programs for people with visual impairments, the creation of scientific-methodological resource centers for inclusive education, and the integration of such children into general education institutions. The conclusions of the study underline that addressing issues of accessibility, inclusion, and humanization of societal relations towards visually impaired individuals will contribute to their successful socialization and professional training, reflecting modern approaches to education and vocational training for blind and visually impaired individuals. The importance and prospects of implementing inclusive education in Ukraine’s educational space are demonstrated and significant for educators, lecturers, and students of pedagogical and technical universities, as well as education and science professionals.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 522
by E. C. Garwe, M. Zunguze, M. Kanda
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
This study assesses the role and process of accreditation in enhancing the quality and efficacy of higher education institutions in Zimbabwe, with a specific focus on the transformative effects this process has on educational standards. Using Zimbabwe Ezekiel Guti University (ZEGU) as a case study, the research examines the programme accreditation process, the challenges, and the success factors thereof. The study adopts a qualitative approach, with in-depth interviews with participants across administration, faculty, and students and document reviews. Through findings of the study, we model the multi-stage accreditation process, identifying challenges, key factors, and strategies that contribute to successful accreditation, such as rigorous self-evaluation, robust stakeholder engagement, and compliance with overarching accreditation benchmarks. The research findings present a compelling argument for the integration of accreditation as a central component of quality assurance across the higher education spectrum. The implications of this study stretch across borders, offering evidence-based recommendations for policymakers and educators to reinforce their quality assurance systems and thereby fostering an environment conducive to generating graduates prepared for the global workforce. By highlighting the accreditation process as a vehicle for continuous quality improvement, this research positions higher education institutions as pivotal contributors to individual empowerment and societal progress. The research thereby offers insights that are intended to support policy formulation, inform institutional strategies, and guide quality enhancement initiatives across various educational contexts.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1465
by Afam Uzorka, Kagezi Kalabuki, Omotoyosi Aishat Odebiyi
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
In the rapidly evolving landscape of education, the continuous professional development of teachers is essential for maintaining high standards of teaching and enhancing student achievement. In-service teacher training programs, which provide ongoing education and training for currently employed teachers, are a crucial component of this professional development. This study uses a mixed-methods approach to investigate the efficacy of in-service teacher training programs in enhancing student success and teaching quality. To obtain thorough data on their experiences and perspectives, 286 in-service teachers from various schools around Kampala completed a survey. Additionally, 52 in-service teachers were interviewed, providing a comprehensive insight into their experiences. According to the quantitative results, 71% of the respondents had previously taken part in in-service training; 61% reported improvements in the quality of their instruction, and 71% noted improvements in student performance. The chi-square tests and regression analysis results showed that in-service training significantly improved student achievement and teacher quality. These findings were corroborated by the qualitative data, which highlighted themes including improved teaching strategies, increased teacher confidence, enhanced student engagement, impact on student achievement, and teacher motivation and morale. The study also highlights the value of peer cooperation and hands-on workshops in training programs and emphasizes the necessity of ongoing, customized professional development. This study offers a comprehensive knowledge of the efficacy of in-service teacher training programs by integrating quantitative and qualitative data. This understanding will be beneficial for educators and policymakers as they build more effective professional development initiatives.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1595
by Ifeoma Chinyere Umeji
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
This study investigates digital assessment and evaluation practices among lecturers in institutions offering teacher education programs in Anambra State, Nigeria. A quantitative research design was adopted, employing a structured questionnaire to collect data on lecturers’ demographics, utilization of digital assessment tools, perceived benefits and challenges, and factors influencing adoption. The questionnaire, validated for reliability using the Cronbach Alpha method (α = 0.88), was distributed to 110 lecturers selected through convenience sampling. Data analysis included t-tests to examine differences in digital assessment practices based on demographic variables. Ethical considerations were addressed, ensuring participants’ informed consent and confidentiality. The study sheds light on the current landscape of digital assessment practices in teacher education, offering insights for improving pedagogical approaches and enhancing educational outcomes in Anambra State.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1501
by Wentao Liu, Hanwei Wu
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
Previous research underscores the pivotal role of AI in advancing second language (L2) learning, yet gaps persist in understanding how individual differences shape L2 learners’ perceptions of AI resources. Addressing this gap, this study explored the impact of demographic characteristics (age and gender) and personality traits (extroversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and openness) on attitude toward AI-assisted L2 learning. This attitude encompasses the opinions, feelings, and beliefs individuals hold about using AI as a tool to facilitate L2 learning. Data were collected from 493 L2 learners enrolled in Chinese colleges through an online questionnaire using two validated scales. Through SPSS 26, descriptive statistics indicated a moderately high positive attitude among students. Multiple regression analyses revealed that older students and females exhibited more favorable attitude compared to their younger and male counterparts, respectively. Additionally, personality traits—excluding agreeableness—significantly influenced attitude. Besides, extroversion and neuroticism negatively predicted attitude, whereas conscientiousness and openness had positive predictive effects. Moreover, this study discusses theoretical implications and offers educational insights while suggesting avenues for future research.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1488
by Lyn Johnston, Alan Johnston
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
Education is considered a tool for addressing issues in society. This paper identifies the role of education and how it fits with social theory. Through focusing on vocational education this article considers issues to address challenges within UK productivity, focusing on post-compulsory 16–19 years old education. The article finds that there is a limited appreciation of vocational education by society and that there have been numerous attempts to achieve parity with A levels, which has never been achieved. The article ends by providing a reflection on whether it is too early to tell and sets the challenge that while it is important to see if T levels, which were introduced in September 2020, do improve productivity and economic prosperity, it is more important to research whether they actually create parity within the qualification structure.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1395
by Hossein Isaee, Hamed Barjesteh
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
The outbreak of coronavirus in 2020 posed a significant challenge for English Language Teaching (ELT) instructors, who were obliged to transform their face-to-face classes into virtual and online ones overnight. In this new, unfamiliar context, it was crucial to keep students constantly engaged, motivated, and interested in learning. Nonetheless, rather than merely taking into account the pessimistic facets of this paradigm shift, many scholars and experts tried to concentrate on the chances that remote/online context presents for language learning and teaching communities. In effect, “Engaging Online Language Learners” is a practical book, the authors of which have considered the sudden shift online connected with the pandemic as an opportunity to enhance the inclusivity of language learning while testifying that EFL/ESL learners’ engagement in a remote/online language learning context ought to be an inevitable priority. Being well targeted to its ELT audience and deeply grounded in both principles of learning engagement and foreign language teaching theories, the book straightly targets language teachers, whether experienced ones or those who intend to teach online for the first time. It also bestows ELT teachers with a clear road map to discern what the next steps are for innovative practices in online/remote learning and teaching contexts.
 Open Access
Open Access
Perspective
Article ID: 1444
by Md. Saiful Alam, Adelina Asmawi
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
The domains of artificial intelligence (AI) and the field of education have an extending history of complementary advances and a co-evolutionary trajectory. Following this trajectory, the contemporaneity of the cited co-evolution has been tracked down in the most recent introduction of Edu GPT for campuses. In this commentary, we offer some procedural considerations and sort out some prerequisites that would serve as the prelude to Edu GPT’s embrace in higher education. As opposed to the wholesale adoption of this updated GPT in higher education, we advocate for a glocalized approach that relies on epistemic guidance to make historically informed decisions about welcoming or rejecting this GPT tool. The potentially catastrophic effects of blindly embracing of Edu GPT can be avoided by pragmatized alternative mechanisms for balanced and responsible uses of the tool. Besides, contextual diversities have to be especially considered while the approach further calls for a structural episodic implementation stages: (a) design, (b) development, (c) adoption, (d) monitoring, and (e) normalization. We further characterize the adoption method by criticality and decolonization as a reaction to Edu GPT’s western-data-centric epistemic colonization. Furthermore, before implementing Edu GPT in higher education, it is imperative to establish an evidence-based AI proficiency framework and detection infrastructure. In the same vein, teachers’ modeling is needed for students to follow when it comes to employing Edu GPT in academic activities as a norm.
 Open Access
Open Access
Opinion
Article ID: 1398
by Anna Tenieshvili
Forum for Education Studies, Vol.2, No.3, 2024;
The current opinion article represents a set of recommendations and pieces of advice related to the development and integration of the curriculum of an English-language educational program (ELEP) at maritime education and training institutions (METIs). The title of the article implies integration of the curriculum of the educational program that would entirely be taught in the English language. In my opinion, such an educational program and its alumni would help METI meet the demands of the modern international maritime labour market. The paper could be interesting and useful for higher education institutions that are oriented on the complete transition of the educational process to an English-language educational program that would be delivered only in the English language. Nowadays there are a lot of educational institutions in the world where educational processes are mainly conducted in native language, and the recommendations given in the present opinion article could be applied by these institutions for the development of the curriculum of ELEP. Consideration of curriculum design is the main topic of the present paper that comprises the most significant issues and details of the topic.