
Oasi Research Institute-IRCCS, Italy

This issue centers on people's psychological phenomena in the contemporary era, particularly their consumption psychology in the digital economy and the impact of COVID-19 on medical staff and patients' mental health. These studies indicate that people's psychological states are directly tied to the context of the times, and it is especially vital to learn to adapt to changes caused by the context of the times.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 417
by Paraskevi Theofilou, Konstantina Papaemmanouil
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
Background: Frequently, the contribution of exercise to the elderly and the associated benefits of such activities are discussed. Aim: This paper deals with the contribution of exercise to the levels of quality of life, fatigue, and pain management. Method: Then, quantitative and cross-sectional research is carried out to investigate the contribution of physical exercise to the levels of quality of life, fatigue, and pain management in women over 60 years of age. For the data collection, the questionnaire used consisted of the Missoula—VITAS Quality of Life Index (MVQOLI), the Pain Assessment Questionnaire (PSeQ), and the Fatigue Assessment Scale (FAS). Results: From the statistical analysis made between exercise and quality of life, fatigue, and pain management of the women over 60 who participated in the research, it follows that women undergoing exercise show a better quality of life and less fatigue, while no statistically significant difference was detected in terms of pain management. Conclusion: It seems that exercise positively affects quality of life and fatigue. Potential implications must be addressed in order to organize more exercise programs, particularly for older people.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 390
by Alan Johnston
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
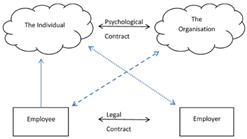
The level of research undertaken on the academic psychological contract, and its influence on academics’ behaviour is limited. This paper seeks to consider the academic psychological contract, by reviewing its manifestation within the role and the influence on their undertaking of the role. Particularly important is academics’ interpretation of the role and what they consider important. Within this, the paper considers in-role and extra-role activities and what may be the grey areas in which time is spent. The research adopts the combined usage of phenomenology with interpretivist processes to investigate the insights of eighteen academics at nine UK University Business Schools. Semi-structured interviews were used to collect data to consider the constructs’ manifestation. Key aspects of behaviour were identified as discretionary effort autonomy and managerialism, with links to academic citizenship.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 504
by Seyyedeh Sahar Asgari Ghalebin, Akbar Atadokht, Seyyedeh Mahsa Mousavi
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
There are four parenting styles based on two indicators of parental affection (parental responsiveness) and parental control (parental strictness). When there is no balance between the love and strictness of the parents, the child sees various damages in different psychological, biological, and social dimensions. These injuries can be continuous and overshadow his whole life. This article is a comprehensive review of the life of a 21-year-old girl with an authoritarian parenting style, i.e., low affection and high strictness. The mother has grown up, and this way of interacting with her continues from the mother’s side. Various results have shown that this girl, like her peers, has lost the ability to manage her life and basic human functions such as judgment, decision-making, planning, proper interpersonal communication, continuing education, and recognizing her interests and identity. It has become a robot that only obeys its mother and substitutes for the source of power to gain their satisfaction.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1255
by Victor Matheus Lopes Martinez, Sophia Gielow Marrero
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
The present study had the general objective of evaluating the relationship between physical activity and mental health in older adults. For this, a cross-sectional survey was carried out with 35 older adults aged between 60 and 76 years old (65.31 ± 4.50). To assess the level of physical activity, the six-minute walk test (6MWT) was used, while mental health was measured using the geriatric depression scale (GDS). A comparison was made between the physically active and inactive groups (classified by the 6MWT) using the Student’s t-test for GDS scores. In addition, the Ancova test was performed to compare groups for mental health outcome (GDS). The results show us that the mean age of the individuals was 65.31 with a standard deviation of 4.50. Among the older adults, 12 were classified as physically active and 23 as inactive. However, the main finding of this study lies in the difference between the groups for the mental health outcome, since the physically active group had a mean GDS lower (Mean = 3.33) than the physically inactive group (Mean = 7.30), with statistical significance (p = 0.05). This is in line with the literature on the benefits of physical activity in preventing and reducing mental disorders. The study makes room for further studies, especially clinical and longitudinal trials, in order to better understand these real impacts of physical activity.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1217
by Verlin B. Hinsz
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
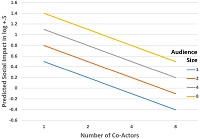
This experiment examined the influences of the number of co-actors and audience size on manual dexterity task performance and subjective reactions such as perceived effort and arousal. Predictions derived from social impact theory and the self-attention perspective’s other-total ratio indicated that both the number of co-actors and audience size should influence responses. Undergraduate students (N = 128) responded as 1, 2, 4, or 8 group members who were observed in a counterbalanced fashion by 1, 2, 4, or 8 audience members for four performance trials. The predictions of increased task performance with larger audience sizes and decreased performance as the number of co-actors increased were not supported. Participants rated arousal as somewhat consistent with the predictions from the self-attention perspective and social impact theory. Self-reported effort was consistent with the predicted patterns, but not always significantly so. The influence of the number of others is moderated by the objective-subjective nature of the responses of real co-actors performing in front of live audiences.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1233
by Karolina Krupa-Kotara, Dominik Gorzawski, Beata Nowak, Katarzyna Barylska, Paweł Juraszek, Mateusz Grajek
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
Obesity is not only a medical problem, but also a psychological one. People with obesity often experience stigma, discrimination, and prejudice, which can lead to low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety. In addition, unhealthy eating habits are often linked to emotions such as stress, sadness, or boredom, which can lead to eating in excess. For this reason, understanding the psychological aspects of obesity is important for effective intervention in this area. Many factors influence the development of obesity, including genetic, hormonal, environmental, and behavioral factors. One of the most important factors is lifestyle, particularly eating habits. People with obesity are often characterized by unhealthy eating habits, such as high-calorie and processed foods, a lack of meal regularity, and excessive consumption of sweets and sweetened beverages. This article focuses on the relationship between psychological factors and eating behavior in people with obesity. Gathering this information is important for understanding what factors may influence the development and persistence of obesity and what psycho-dietetic strategies may be effective in changing eating habits and reducing weight.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1281
by Wai Lun Lam, Keng Tou Chau, Chun Cheong Wong, Adrian Low, Ming Hang Chan, Cheuk Chi Chung, Nga Yan Kwok, Lai Kiu Tsang
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
Rope Therapy, a novel complementary therapy, combines professional rope techniques and professional comprehensive sensory integration training program, treatment, and training programs for people with special educational needs for the sake of enhancing their vestibular sense, proprioception, muscle tension, and whole body coordination ability by stimulating the brain nerves and secretion of neurotransmitters. Method: Rope therapy is conducted with the model “Home-based Rope Therapy Program” for 12 weeks. Parents who attended this program are required to accept training and assessment. To conduct the therapy independently, parents have to learn how to use the tools of this home-based rope therapy and interact with children during the training. In this study, children had intensive rope exercise training at home with positive feedback from parents within this period leading to higher emotional control and concentration level, more eye contact, and emotional and wording expression. The family would also receive feedback from the teachers, other professional trainers, and sports coaches related to the condition of the children. Result: A total of 69 families participated in the survey with children aged 4 to 26, including those who were diagnosed or had a suspicion of the autism spectrum, hyperactivity and inattention, dyslexia, and other special needs. After 12 weeks of home training, the result showed that the child’s concentration levels and control of negative emotions have been significantly improved. Meanwhile, it has been proven that the “Home-based Rope Therapy Program” is effective in bringing positive interactions and emotions to children and families. Conclusion: “Home-based Rope Therapy Program” provides children with intensive rope exercise training at home, satisfying children’s physical and sensory needs. Also, this program increases children’s exercise in muscle strength, balance, and coordination leading to higher concentration levels and high-quality parent-child time, thereby improving school children’s emotional control and concentration, and enhancing family harmony.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1339
by Ushba Rasool, Muhammad Hammad Hussain Shah, Rehan Muhammad, Min Gao, Huang Wang, Babar Nawaz Abbasi
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
Bilingualism and multilingualism are no longer exceptional occurrences on today’s globe; instead, they have become the prevailing standards in cultures worldwide. Individuals can become bilingual by either simultaneous acquisition of two languages from childhood or sequential acquisition over time as bilinguals. The primary objective of this study is to determine the role of language therapists in assisting parents and teachers in optimizing the dual-language proficiency of young children. This case study was conducted to investigate this matter, and it was determined that a balanced utilization of both languages, coupled with guidance from language professionals to parents and teachers, dramatically enhances a child’s performance. In addition, parents consistently strive for their child to become multilingual, as they perceive it as a beneficial factor for their child’s future. The data was gathered through a semi-structured interview session with parents and real-life scenario observations. This case study illustrates the advantages and disadvantages of being bilingual or multilingual. The study findings will assist parents and early childhood educators in dealing with children coping with different language encounters at home and school.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1365
by Reshmi Dutta, Rita Karmakar
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
Introduction: Human beings generally feel stressed at some point in life. Internet addiction disorder is increasingly gaining attention as individuals use the internet excessively as a maladaptive way to cope with daily life stress. Objective: The paper aims to find out the level of internet addiction with respect to gender, age groups, and family type, to determine the difference (if any) between males and females with respect to internet addiction, the difference (if any) in internet addiction with respect to age groups, and the difference (if any) between nuclear and joint family types with respect to internet addiction. Method: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 140 participants (71 male and 69 female) from Kolkata, West Bengal. Findings: It shows a statistically significant difference in internet addiction mean scores between males and females. It also indicates that participants under 25 years of age have higher mean scores than those over 25 years. The next part reveals that individuals in nuclear families have higher mean scores than those in joint families, regardless of gender and age group, and finally indicates a statistically significant interaction effect of age group with gender and family type. Conclusion: Gender significantly affects internet addiction mean scores, with females under 25 in nuclear families being more addicted than their counterparts.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1362
by Mohammad Shahidul Islam , Muhammad Ali, Fariba Azizzadeh
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
This conceptual paper examines the influence of psychological principles on consumer decision-making within digital shopping environments, integrating psychological theories with empirical observations to understand how cognitive, emotional, and social factors shape consumer behaviors online. By reviewing existing literature and applying a constructivist epistemology and relativist ontology, the study develops a conceptual framework highlighting the impact of digital interface design, information availability, and personalized marketing on consumer choices. The paper analyzes various examples and identifies vital psychological triggers and decision-making barriers, offering strategic insights for enhancing digital marketing practices. This research contributes to academic and practical understandings of digital consumer behavior, proposing that a more profound integration of psychological insights can lead to more effective and ethically grounded marketing strategies in the digital era.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1274
by Md Moyaje Uddin, Yanling Cai, Tamzida Fatima
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
This research mainly focuses on examination of the digital marketing buyer’s perspective with reference to select e-commerce companies. The consumer behavior is always changing in nature which is evident from various studies that have been conducted in the field of marketing. The digital marketing provides the consumer with lot of information about product, price ranges, alternatives and substitutes and other core dimensions of the product. The main objective of this research is to determine the factors that are influencing the consumers and their perception towards buying the products that are marketed digitally. Dhaka is one of the developing cities to investigate the online buyer’s expectation level and their perceptions towards digital marketing. Semi structured interviews for qualitative data and e-commerce websites, magazines, digital marketing books, periodicals and Internet were approached for secondary data. The primary data were collected from 692 online buyers from 4 revenue divisions in Dhaka district through non-probability sampling technique. Structural equation modeling has been used in this research for the data analysis. It is found that the frequency of online purchases has been increasing among the buyer of Dhaka district, which is evident from the response of the consumers, involved in the study. The results stated that the e-commerce company Amazon is performing well in the study area as per the opinions of the consumers involved in study. The future growth of the digital marketing is depending on the expansion strategies of companies which aim to provide consumers with constructive promotional offers, promising after sales services and protecting the financial information of the consumers of online platforms.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 358
by Anna Bilali, Frosyna Anagnosti, Pinelopi Stamati, Kiriaki Gatanas, Nikolaos Thalassinos, Agis Terzidis
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people’s lives is dramatic. The relationship between Brain Fog and Long-COVID, the consequences for the mental health of patients, and its treatment are the objectives of this systematic review. An electronic search was carried out, and the databases searched included PubMed, Emerald, EMBASE, and Science Direct. Regarding the review, data collection included English papers with full bibliographies, abstracts, and keywords, published in electronic form in the last 2 years (2020–2022). The findings indicate the importance of a holistic approach and treatment for Post-COVID Brain Fog. It is also necessary for healthcare workers to investigate the biological and psychosocial background of Brain Fog symptoms in detail to provide the appropriate health service. However, more scientific studies are needed on the effectiveness of treatment approaches for the benefit of public health and well-being.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 359
by Marika Wlazło, Daria Łaskawiec-Żuławińska, Mateusz Grajek, Ilona Korzonek-Szlacheta
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
The overall impact of pandemics on the healthcare sector has been substantial and multidimensional, presenting numerous challenges that have affected healthcare workers on various fronts. Pandemics, particularly the COVID-19 epidemic, caused destabilization in healthcare systems, creating complex challenges for both medical staff and patients. During the pandemic, healthcare professionals faced exceptionally difficult working conditions, such as increased workload, inadequate medical resources, and the pressure of making challenging moral decisions, for instance, related to the allocation of limited resources during a crisis. These factors increased the risk of occupational burnout—a state that may manifest as emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and decreased self-esteem and efficacy. Occupational burnout among healthcare workers is a highly significant phenomenon because it can directly impact the quality of care provided to patients. Higher levels of burnout are associated with an increased risk of medical errors, decreased work engagement, and reduced empathy in patient interactions. Additionally, individuals experiencing burnout may encounter reduced social support, further complicating the issue. Consequently, the negative consequences of occupational burnout can have a long-term impact on healthcare workers themselves, the quality of medical care, and patient-provider relationships. Therefore, managing the risk of burnout among medical staff becomes a crucial challenge not only for the mental health of healthcare workers but also for ensuring high-quality healthcare for society. Providing psychological support, proper human resource management, and promoting a healthy lifestyle among medical personnel are essential to alleviating the psychological burden on workers and ensuring sustained, high-quality healthcare.
 Open Access
Open Access
Review
Article ID: 1401
by Paweł Juraszek, Mateusz Grajek
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
The discussion concerns social acceptance of people with chronic diseases, covering the definition of acceptance, its determinants, stereotypes, and groups of diseases that most often face social reluctance. Social acceptance is a key element of healthy social functioning and implies agreement that people with chronic diseases exist, are respected and treated equally with healthy people. It is a process dependent on education, personal experience, social support and culture. Research indicates that people with mental illness, HIV/AIDS, skin diseases and obesity often experience stigma and discrimination. In particular, people with mental illnesses face negative stereotypes, such as being seen as dangerous and unable to function in society. People living with HIV/AIDS are often victims of social ostracism due to fear of infection and moral judgments. Skin diseases such as psoriasis and obesity also lead to social isolation and discrimination. Another group is people with cancer, who often experience social resentment due to fear, ignorance and stereotypes associated with the disease. Social education and psychological and social support are key to reducing stigma and improving the quality of life for these people. Practical measures to increase social acceptance include: educational programs, media campaigns, psychological support, legislative changes, and local and community initiatives. All of these activities can help reduce stigma and discrimination against people with chronic diseases, promoting greater empathy and understanding in society.
 Open Access
Open Access
Book Review
Article ID: 1120
by Feng Mao, Jiaqin Li
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.3, No.1, 2024;
N/A