Psychological correlates of obesity
Abstract
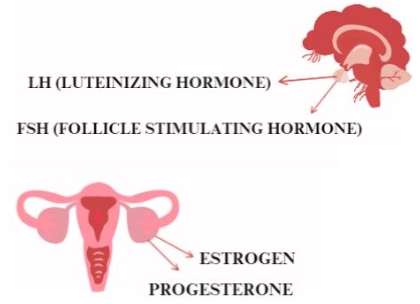
Obesity is not only a medical problem, but also a psychological one. People with obesity often experience stigma, discrimination, and prejudice, which can lead to low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety. In addition, unhealthy eating habits are often linked to emotions such as stress, sadness, or boredom, which can lead to eating in excess. For this reason, understanding the psychological aspects of obesity is important for effective intervention in this area. Many factors influence the development of obesity, including genetic, hormonal, environmental, and behavioral factors. One of the most important factors is lifestyle, particularly eating habits. People with obesity are often characterized by unhealthy eating habits, such as high-calorie and processed foods, a lack of meal regularity, and excessive consumption of sweets and sweetened beverages. This article focuses on the relationship between psychological factors and eating behavior in people with obesity. Gathering this information is important for understanding what factors may influence the development and persistence of obesity and what psycho-dietetic strategies may be effective in changing eating habits and reducing weight.
References
Al-Kandari, Y. Y., & Crews, D. E. (2012). College obesity: emotional distress, body image disturbance, and binge eating among males and females. Journal of American College Health, 60(1), 43-50.
Bandura, A. (2004). Health Promotion by Social Cognitive Means. Health Education & Behavior, 31(2), 143–164. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090198104263660
Bandura, A. (2021). Psychological Modeling. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003110156
Bessesen, D. H. (2018). Obesity assessment and management. Med Clin North Am, 102(1), 1.
Boggiano, M. M., Wenger, L. E., Turan, B., et al. (2015). Investigating the role of emotional eating in weight management: Challenges and opportunities. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 1-14.
Bourne, M. J., Smeltzer, S. C., & Kelly, M. M. (2021). Clinical teacher self-efficacy: A concept analysis. Nurse Education in Practice, 52, 103029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2021.103029
Bray, G.A., Kim, K.K., Wilding, J. P. H., et al. (2017). Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes Rev, 18(7), 715-723. https://doi.org/10.1111/obes.12551
Brownell, K. D., Farley, T., Willett, W. C., et al. (2009). The Public Health and Economic Benefits of Taxing Sugar-Sweetened Beverages. New England Journal of Medicine, 361(16), 1599–1605. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmhpr0905723
Camargo, C. A., Weiss, S. T., Zhang, S., et al. (1999). Prospective Study of Body Mass Index, Weight Change, and Risk of Adult-onset Asthma in Women. Archives of Internal Medicine, 159(21), 2582. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.159.21.2582
Carels, R. A., Darby, L., Cacciapaglia, H. M., et al. (2005). Applying a stepped-care approach to the treatment of obesity. J Psychosom Res, 59(6), 375–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2005.04.006
Cawley, J., & Meyerhoefer, C. (2012). The medical care costs of obesity: An instrumental variables approach. Journal of Health Economics, 31(1), 219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhealeco.2011.10.003
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Adult Obesity Causes & Consequences. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/causes.html (accessed on 20 April 2024).
Chamorro, R., Flores-Ortiz, R. (2010). Personality traits and eating behavior in the general population. Revista de Psicologia y Salud, 21(3), 293-299.
Chetcuti, L., Uljarević, M., Ellis-Davies, K., et al. (2021). Temperament in individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 85, 101984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2021.101984
Cierpiałkowska, R., Siwek M., Wolak, M., et al. (2014). Temperament and character traits of obese subjects. Psychiatria Polska, 48(4), 673-686.
Czajkowska, A., Oblacińska, A., Jodkowska, M. (2017). Psychological Determinants of Obesity in Children and Adolescents - a Systematic Review. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, 24(4), 595-602. https://doi.org/10.26444/aaem/79627
Danese, A., & Tan, M. (2013). Childhood maltreatment and obesity: systematic review and meta-analysis. Molecular Psychiatry, 19(5), 544–554. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.54
Erskine, H. E., & Whiteford, H. A. (2018). Epidemiology of binge eating disorder. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 31(6), 462–470. https://doi.org/10.1097/yco.0000000000000449
Felson, D. T. (1988). Obesity and Knee Osteoarthritis. Annals of Internal Medicine, 109(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-109-1-18
Fontaine, K. R., & Barofsky, I. (2001). Obesity and health‐related quality of life. Obesity Reviews, 2(3), 173–182. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1467-789x.2001.00032.x
Gajda, E., Biskupek-Wanot, A. (2020). Stress and its effects. In: Biskupek-Wanot, A., Wanot, B., Kasprowska-Nowak, K. (editors). Physical activity and stress issues. Wydawnictwo Naukowe Uniwersytetu Humanistyczno-Przyrodniczego im. Jana Długosza w Częstochowie.
Galvin, B. M., Randel, A. E., Collins, B. J., et al. (2018). Changing the focus of locus (of control): A targeted review of the locus of control literature and agenda for future research. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 39(7), 820–833. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2275
Gibson, E. L. (2012). Emotional influences on food choice: sensory, physiological and psychological pathways. Physiology & behavior, 107(4), 643-651.
Gu, D., & Dupre, M. E. (2021). Encyclopedia of Gerontology and Population Aging. Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22009-9
Hu, F. B. (2011). Globalization of Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 34(6), 1249–1257. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-0442
Inzlicht, M., Werner, K. M., Briskin, J. L., et al. (2021). Integrating Models of Self-Regulation. Annual Review of Psychology, 72(1), 319–345. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-061020-105721
Kahan, S., Manson, J. E. (2018). Obesity management: Update on lifestyle therapy and bariatric surgery. Circulation, 137(10), e201-203.
Kesavayuth, D., Ko, K. M., & Zikos, V. (2018). Locus of control and financial risk attitudes. Economic Modelling, 72, 122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2018.01.010
Kessler, R. C., Berglund, P. A., Chiu, W. T., et al. (2013). The Prevalence and Correlates of Binge Eating Disorder in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Biological Psychiatry, 73(9), 904–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.11.020
Klassen, R. M., & Klassen, J. R. L. (2018). Self-efficacy beliefs of medical students: a critical review. Perspectives on Medical Education, 7(2), 76–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-018-0411-3
Konttinen, H., Haukkala, A., Sarlio-Lähteenkorva, S., et al. (2010). Emotional eating, depressive symptoms and self-reported food consumption. A population-based study. Appetite, 14(8), 1045-1054.
Konttinen, H., Sarlio-Lähteenkorva, S., Silventoinen, K., et al. (2018). Emotional Eating, Depression and Overweight Among Finnish Adults: A Population-Based Study. Appetite, 1(2), 347-354. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2004.05.007
Krupa-Kotara, K., Dakowska D. (2019). The impact of obesity on cancer: a review of the literature. Journal of Educational, Health and Sport, 9(7), 263-277.
Labella, M. H., & Masten, A. S. (2018). Family influences on the development of aggression and violence. Current Opinion in Psychology, 19, 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.03.028
Luciano, M., Janiri, D., Fiorillo, A., et al. (2020). Clinical Picture, Temperament, and Personality of Patients with Mixed States. Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 43(1), 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psc.2019.10.002
Luppino, F. S., de Wit, L. M., Bouvy, P. F., et al. (2010). Overweight, Obesity, and Depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 67(3), 220. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.2
Malnick, S. D., Knobler, H. (2016). The medical complications of obesity. QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, 109(7), 423-440.
Mason, S. M., Flint, A. J., Roberts, A. L., et al. (2014). Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms and Food Addiction in Women by Timing and Type of Trauma Exposure. JAMA Psychiatry, 71(11), 1271. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1208
Morin, A. (2011). Self‐Awareness Part 1: Definition, Measures, Effects, Functions, and Antecedents. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 5(10), 807–823. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2011.00387.x
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (n.d.). Health Risks of Being Overweight. Access protocol: Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/health-risks-overweight (accessed on 20 April 2024).
Ogden, J. (2003). The role of peer models in the development of weight-related behaviors. Obesity research, 11(2), 5-11.
Ogden, C. L., Carroll, M. D., Kit, B. K., et al. (2012). Prevalence of Obesity and Trends in Body Mass Index Among US Children and Adolescents, 1999-2010. JAMA, 307(5), 483. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.40
Oldham, M. A. (2020). Personality-Informed Care: Speaking the Language of Personality. Psychosomatics, 61(3), 220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psym.2020.01.005
O'Neil, P. M., Jarrell, M. P. (2013). Psychological aspects of obesity. Medsurg Nursing, 22(4), 238-242.
Powell-Wiley, T. M., Ayers, C. R., de Lemos, J. A., et al. (2014). Disparities in physical activity and sedentary behaviors among US children and adolescents: prevalence, correlates, and intervention implications. Journal of public health policy, 35(1), 67-90.
Pronk, N. P., & Kottke, T. E. (2009). Physical activity promotion as a strategic corporate priority to improve worker health and business performance. Preventive Medicine, 49(4), 316–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2009.06.025
Pugh, M., Waller, G., & Esposito, M. (2018). Childhood trauma, dissociation, and the internal eating disorder ‘voice.’ Child Abuse & Neglect, 86, 197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2018.10.005
Puhl, R. M., & Heuer, C. A. (2009). The Stigma of Obesity: A Review and Update. Obesity, 17(5), 941–964. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2008.636
Quick, V. M., Byrd-Bredbenner, C., & White, A. A. (2013). Overweight, obesity, and collegiate academic performance. Journal of American college health, 61(5), 280-287.
Redelmeier, D. A., Najeeb, U., & Etchells, E. E. (2021). Understanding Patient Personality in Medical Care: Five-Factor Model. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 36(7), 2111–2114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-021-06598-8
Renehan, A. G., Tyson, M., Egger, M., et al. (2008). Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet, 371(9612): 569-578. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60269-X
Rettew, D. C., & McKee, L. (2005). Temperament and Its Role in Developmental Psychopathology. Harvard Review of Psychiatry, 13(1), 14–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/10673220590923146
Robinson, E., Blissett, J., & Higgs, S. (2013). Social influences on eating: implications for nutritional interventions. Nutrition Research Reviews, 26(2), 166–176. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954422413000127
Roehling, M. V., Roehling, P. V., Pichler, S. (2007). The relationship between body weight and perceived weight-related employment discrimination: the role of sex and race. J Vocat Behav, 71(2), 300-318. doi:10.1016/j.jvb.2007.05.002
Sánchez-Villegas, A., Martínez-González, M. Á., Toledo E., et al. (2015). Psychological Factors and Food Habits in Spanish Adults. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 105(11), 1712-1719. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2005.08.027
Schwarzer, R., & Renner, B. (2000). Social-cognitive predictors of health behavior: Action self-efficacy and coping self-efficacy. Health Psychology, 19(5), 487–495. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-6133.19.5.487
Singh, A. S., Mulder, C., Twisk, J. W. R., et al. (2008). Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obesity Reviews, 9(5), 474–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789x.2008.00475.x
Stepaniak, U., Micek, A., Waśkiewicz, A., et al. (2016). Prevalence of general and abdominal obesity and overweight among adults in Poland. Results of the WOBASZ II study (2013–2014) and comparison with the WOBASZ study (2003–2005). Polish Archives of Internal Medicine. https://doi.org/10.20452/pamw.3499
Story, M., Kaphingst, K. M., Robinson-O’Brien, R., et al. (2008). Creating Healthy Food and Eating Environments: Policy and Environmental Approaches. Annual Review of Public Health, 29(1), 253–272. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.publhealth.29.020907.090926
Suliga, A., Dolińska, M., & Kędra, E. (2022). Methods and techniques of coping with stress in the work of a nurse. Investing in Nursing and Respecting Nurses’ Rights-Controversies and Challenge, 73.
Tan, S., & Yip, A. (2018). Hans Selye (1907–1982): Founder of the stress theory. Singapore Medical Journal, 59(4), 170–171. https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2018043
Tasca, G. A. (2019). Attachment and eating disorders: a research update. Current Opinion in Psychology, 25, 59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2018.03.003
Teixeira, P. J., Silva, M. N., Mata, J., et al. (2012). Motivation, self-determination, and long-term weight control. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 9(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-9-22
Terracciano, A., Sutin, A. R., Sanna, S., et al. (2009). Major personality traits and adiposity in 6, 821 middle-aged and older adults: the Sardinia Study. Obesity, 17(12), 2283-2288.
The GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators. (2017). Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. New England Journal of Medicine, 377(1), 13–27. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1614362
Torres, S. J., & Nowson, C. A. (2007). Relationship between stress, eating behavior, and obesity. Nutrition, 23(11–12), 887–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2007.08.008
Udo, T., & Grilo, C. M. (2018). Prevalence and Correlates of DSM-5–Defined Eating Disorders in a Nationally Representative Sample of U.S. Adults. Biological Psychiatry, 84(5), 345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.03.014
Van den Berg, L., Pieterse, K., Malik, J. A., et al. (2011). Cognitive control and eating behavior in obesity. Journal of behavioral medicine, 34(6), 423-431.
Vancampfort, D., Vanderlinden, J., De Hert, M., et al. (2013). A systematic review of physical therapy interventions for patients with anorexia and bulemia nervosa. Disability and Rehabilitation, 36(8), 628–634. https://doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2013.808271
Volkow, N. D., Wang, G. J., Fowler J. S., et al. (2008). Overlapping neuronal circuits in addiction and obesity: evidence of systems pathology. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 363(1507):3191-200. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0107
Waldman, I. D., Rhee, S. H., LoParo, D., et al. (2018). Genetic and environmental influences on psychopathy and antisocial behavior. The Guilford Press.
Womble, L. G., Williamson, D. A., Martin, C. K., et al. (2009). Psychosocial variables associated with binge eating in obese males and females. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 42(6), 505-510.
World Health Organization. (n.d.). Obesity and overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 20 April 2024).
Yusuf, S., Hawken, S., & Ounpuu, S. (2005). Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. Lancet, 366(9497), 1640-1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67663-5
Zappetti, D., & Avery, J. D. (2019). Medical Student Well-Being. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16558-1
Copyright (c) 2024 Karolina Krupa-Kotara, Dominik Gorzawski, Beata Nowak, Katarzyna Barylska, Paweł Juraszek, Mateusz Grajek

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.