
University of Chile, Chile

 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 461
by P. R. Sekhar Reddy
Materials Technology Reports, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
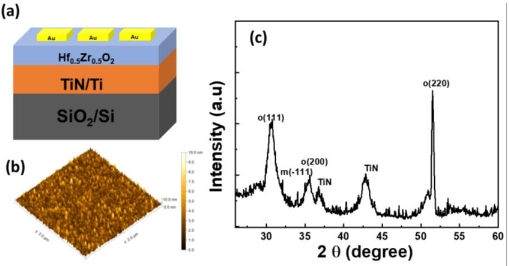
In this study, Zr-doped HfO2 (HZO) based resistive random-access memory (RRAM) device were fabricated. The Hf:Zr (1:1) ratio in the HZO films were controlled by changing the HfO2 and ZrO2 cycle ratio during the atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. Next, we studied the structural and electrical properties of the Au/HZO/TiN RRAM device structure. The RRAM devices exhibits an excellent resistance ratio of the high resistance state (HRS) to the low resistance state (LRS) of ~103 A, and as well as good endurance (300 cycles) and retention (>103 s), respectively. Further, the device showed different conduction mechanism in LRS and HRS modes. The lower biased linear region is dominated by ohmic conductivity, whereas the higher biased nonlinear region is dominated by a space charge limited current conduction. This device is suitable for application in future high-density nonvolatile memory RRAM devices.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 483
by M. Shamshi Hassan
Materials Technology Reports, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
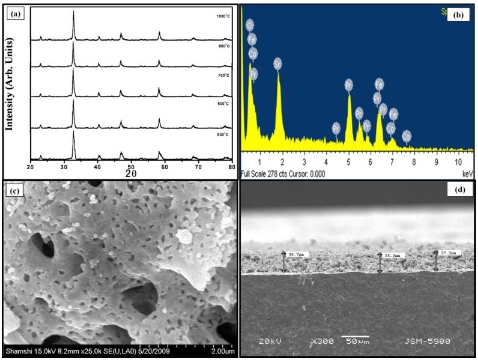
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) are renowned for being effective energy sources that have potential to influence how energy is developed in future. SOFCs operate at low temperatures provides different benefits for widespread commercialization. In the present study a perovskite material Pr0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Co0.2O3−δ (PSFCo) was investigated as cathode for SOFC in intermediate temperature range. Glycine nitrate process was used for the preparation of the samples. PSFCo exhibited cubic structure having small particle size (100–200 nm). The electrical conductivity of the PSFCo was measured as function of temperature up to 850 ℃. The sample displayed maximum electrical conductivity of 370 Scm−1 at around 550–600 ℃. The polarization behavior of PSFCo was calculated by means of AC impedance with Sm0.8Ce0.2O2 (SDC) as electrolyte. The value of area specific resistance (ASR) was calculated as 0.146 Ωcm2 at 800 ℃ and 0.248 Ωcm2 at 700 ℃.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1603
by Joseph Abutu, Tsotsi Rikwen Tsoji, Areo Stephen, Aliyuda Dedan Araye, Sunday Albert Lawal, Ayuba Kitaka Rimamtaatang
Materials Technology Reports, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
In this work, sugarcane bagasse and rice husk were used as filler material for the production of agro-based particle board along with low-density polyethylene and coconut shell, with the aim of investigating the effects of varying compositions of constituents on the performance of the developed composite using constant process parameters of moulding pressure (10 MPa), moulding temperature (140 ℃), curing time (10 min) and heat treatment time (1 h). Experimental design was conducted using box-Behnken design (L1533) while multi-response optimization was carried out using grey relational analysis (GRA). The experimental results revealed that changes in percentage composition affect the performance of the composite, and the multi-response optimal performance of the developed bagasse-based particle board (BPB) and rice husk-based particle board (RPB) can be achieved with bagasse or rice husk (30 wt%), coconut shell (30 wt%), and low-density polyethylene (40 wt%). The results of the analysis of variance showed that the performance of the two particle boards is most influenced by the presence of low-density polyethylene (LDPE). Finally, compared to rice husk, bagasse can effectively serve as a preferred substitute for wood in the production of particle board.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1556
by Chun-Ming Liu
Materials Technology Reports, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
The microstructure and negative differential resistance (NDR) effect of nitrogen implanted rutile TiO2 were investigated by measuring the XPS, Raman spectra and current voltage curves. It was found that the light illumination has large influence on the NDR effect. Under the illumination of 60 mW laser light, a large NDR with a small electric field (1250 V/cm) is obtained. This electric field is about three orders smaller than that reported in literature (1×106 V/cm). The electric field induced tunneling is the possible mechanism of electric transport at higher field region. The NDR is thought to be related to the light and nitrogen dopant induced reaction including the destroying of water, the scavenging of electron, and the surface oxidation transform of non-stoichiometric TiO2−x to stoichiometric insulating state. The results of this paper are not only useful in understanding the mechanism of NDR, but also useful in providing an effective method in manipulation NDR.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1650
by Fabien Kenmogne, Emmanuel Foadieng, Olivier Lekeufack Tiokeng, Roger Eno, Martial Nde Ngnihamye, Alphonse Tchoukouabe, Sorel Holsen Wafo Wafo, Moussa Sali, Emmanuel Yamb Bell, Sévérin Nguiya
Materials Technology Reports, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
In order to enhance the value of local materials and contribute to reducing construction costs in Cameroon, rattan waste is used to reinforce compressed earth blocks (CEB). This main work’s objective is the study of the effect of rattan waste on the physical and mechanical properties of CEB. For this, a soil sample taken in the western region of Cameroon, more precisely in Bangangté, was analyzed, the analysis includes the granulometric analysis, the Atterberg limits, and the Proctor test. Then the CEB samples with different rattan waste contents, that is 0%, 2%, 4% and 6%, were developed for a compaction stress of 7.5 MPa. These different samples were characterized through mechanical and physical tests carried out in the laboratory. It appears that the blocks reinforced with 2% of rattan waste have better mechanical characteristics, respectively 0.70 MPa in three-point bending and 3.04 MPa in compression. On the other hand, the presence of rattan wastes has a positive effect on the mechanical behavior of the composite, by increasing its ductility compared to the fragile behavior of the control block, which is observed during crushing. Thus the mechanical properties of CEB improve with the incorporation of rattan waste, which is optimal for a content of 2%. But they increase the material's porosity, and then its sensitivity to water unlike the control CEB.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1654
by Fabien Kenmogne, Roger Eno, Adoum Danao Adile, Blaise Ngwem Bayiha, Gilbert Tchemou, Martial Nde Ngnihamye, Olivier Lekeufack Tiokeng, Steven Kevin Donfang Nobisse, Emmanuel Yamb Bell
Materials Technology Reports, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
This work focuses on the extraction and experimental characterization of pennisetum purpureum fibers extracted from stems and roots, harvested in the Batié Kingdom, in the West Region of Cameroon. After extracting fibers using the boiling water technique, they are chemically treated to improve their properties and performance and to facilitate their incorporation into various composite materials. For the physical characterizations, it is measured: the absolute and apparent densities, the linear mass, the water absorption rate, and the diameter via the microscope. The mean values of the diameters and the measure of their frequency distributions are calculated, followed by the statistical analysis using the maximum entropy principle, in order to find the most probable diameter necessary for technological applications. For the mechanical properties, only the tensile tests are performed, with the determination of the young modulus of both the stems and roots. The results thus obtained showed that the fibers of the stems have an absolute density of (1.35 g/cm3), a linear mass of (54.6 tex), an apparent density of (0.45 g/cm3), a water content of (12.73%), an absorption rate of (142.46%), a porosity of (65.91%), a mean diameter of (7 mm), an elastic modulus of (3.98 GPa), a tensile strength of value of (1186.59 MPa) and an elongation of 16.17%, while the root fibers have an absolute density of (1.34 g/cm3), a linear mass (16.76 tex), an apparent density of (0.37845 g/cm3), a water content of (12.25%), an absorption rate of (193.16%), a porosity of (71.92%), a diameter of (4 mm), an elastic modulus of (1.55 GPa), a tensile strength of a value of (1960.35 MPa) and an elongation of 60.6%. Thus, the fibers of the stems have good mechanical properties, which make them an appropriate material in several applications, such as the reinforcement of composite materials.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1721
by Anas Elhederi, Mansoor Zoveidavianpoor
Materials Technology Reports, Vol.2, No.1, 2024;
This study investigates the utilization of eggshells, a renewable material, as a weighting additive in water-based drilling muds with different exploring concentrations. The primary objectives were to assess the impact of eggshells on the rheological properties of drilling muds and to determine the optimal concentration of eggshells for achieving desired density and stability, drawing comparisons with calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Both eggshell powder (ESP) and CaCO3 effectively increase mud weight to the target density of 8.75 ppg at 30 g. Notably, ESP exhibits favorable rheological properties at 20 g, maintaining low plastic viscosity 2.7, consistent yield points 1.1, and gel strength comparable to CaCO3. Conversely, CaCO3 shows signs of potential deterioration at 30 g indicated by increased viscosity to 3.5 and decreased yield point to 0.5. ESP demonstrates superior filtration performance, displaying a progressive increase in cake thickness with increasing weight 1.32 mm to 3.12 mm compared to the slower cake build-up of CaCO3 0.92 mm to 2.9 mm. Both additives slightly elevate mud pH, potentially enhancing overall stability.