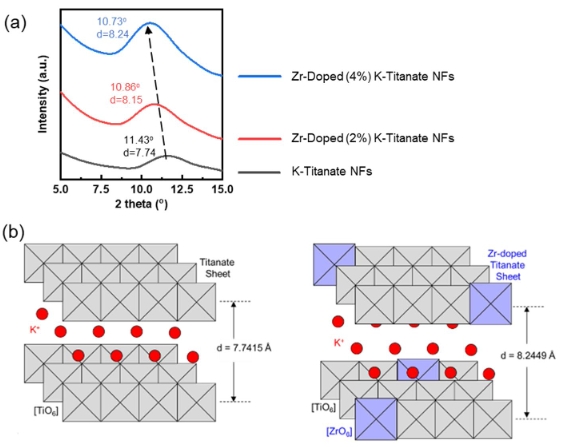
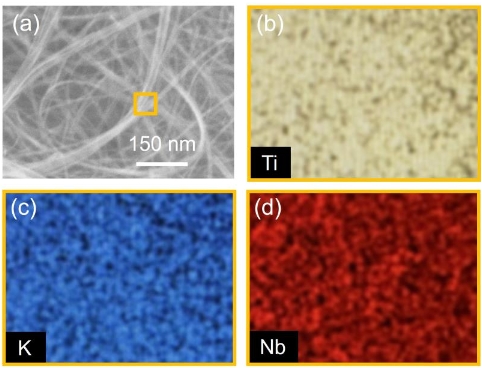
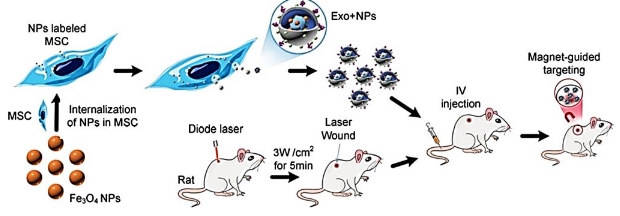
Description
Nano and Medical Materials (NMM, ISSN: 2811-0285) is an open-access journal dedicated to the cutting-edge research at the intersection of nanotechnology and medical materials. It encompasses a broad spectrum of topics from fundamental studies to applied research. The journal places a special emphasis on the latest advances and applications of nanomaterials in biomedicine, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering. By publishing high-quality original research articles and reviews, Nano and Medical Materials serves as a platform for scientists and researchers to exchange and share the latest research findings.
Please see "Focus and Scope" for detailed scope.




 Open Access
Open Access