
Oasi Research Institute-IRCCS, Italy


Applied Psychology Research (APR, eISSN: 3029-276X) is a peer-reviewed, open-access journal that publishes original articles, reviews, research notes, and short communications in the broad field of psychology. The journal seeks original research in all empirical and theoretical fields of psychology, aiming to achieve a deeper understanding of the mental processes of individuals, organizations, and institutions. This includes the cognitive, motivational, affective, and behavioral factors in various situations. It is dedicated to the application of experimental behavioral science research to societal problems, such as social psychology, organizational and leadership psychology, education, economics, management, environment, law, safety, health, and gender issues.
The topics covered in Applied Psychology Research include but are not limited to:
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 2231
by Yonatan Shertzer
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.4, No.1, 2025;
Modern organizations often face challenges implementing initiatives due to the rapidly changing business landscape and encountering internal obstacles like resistance and delays. This research examines the application of the internal and external efficacy model and its effect on resistance to change in work organizations by raising self-efficacy and means-efficacy (a person’s belief in the ability of the tools available to him to perform the task). Raising the two types of efficacies creates a Pygmalion effect in which high expectations for successful performance encourage the investment of efforts; therefore, ultimately, they will lead to more successful performances. In addition, since individuals with an external locus of control place a higher emphasis on resources that are external to them, the moderating effect of the degree of locus of control on the relationship between means-efficacy and resistance to change was studied. The study that included 138 participants was conducted in a logistics and international forwarding company in Israel and examined a change in learning method from face-to-face learning to an asynchronous learning module. During the study, the level of self-efficacy and means-efficacy of participants was raised, and the level of resistance to change and the level of locus of control as a personality trait were measured. The study showed a distinct effect of increasing self-efficacy on the degree of resistance to change (t = −1.66, p < 0.05), but no significant effect of increasing means efficacy on resistance to change was found (t = −0.87, p > 0.05). The effect of means-efficacy on the degree of resistance was found to be moderated by locus of control (t = −2.3, p < 0.05), meaning that those who had an external locus of control were more impacted by the increase in means-efficacy. This means that people with an external locus of control are more affected by means-efficacy than by self-efficacy.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 2580
by Carol Nash
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.4, No.1, 2025;
Migrate as a verb represents a process where providing social services to migrants reduces their instability and discomfort with providers inclined to pity or fear migrants. Consequently, migrants learn to form negative views of themselves, decreasing their mental health. Considering migrate as a verb neglects the noun to whom or to which the migrant is heading—a person, place, thing, event, or idea. Viewing migration as noun-dependent, the migrant is potentially identifiable as self-directing their migration and seeking aid. This study examines examples of the five types of nouns migrants may conceptualize to guide their migration in a narrative review of Google Scholar search results of “[noun-type] to which [whom] migrants head in their migration” for each noun type regarding the four relevant highest returned post-2020 reports. Examining migrant mental health considers a 2023 systematic review regarding place. The purpose is to investigate the social services applicable to migrants if ultimately self-directing (or not) regarding coping theory, contrasting problem-focused with emotion-focused coping. Viewing such migration nouns as essential migration signifiers encourages migrants’ favorable identification. In recognizing the intended self-direction of the migrant, their mental health is improved and is supportable through relevant and appropriately available social services.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 2168
by Sara Akram, Muhammad Sardar Alam
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.4, No.1, 2025;
The present research looks at the effects that social networks use has on the mental health of young users aged between 18 and 25 in the case of Pakistan. Given that social networking sites are becoming more prevalent in the country, there is a growing concern regarding the adverse effects of these sites on the youth. The interviews have been conducted to examine the effects of social networking sites on mental health among the rural and urban population of Pakistan. This study highlights several problems such as social comparison, cyberbullying, sleep disorders, and social media benefits. Social comparison is an issue that social media elevates, as many young adults see posts of others living their desirable lives, wishing to live the same. Trying to live up to such expectations creates pressure within the youth, leading to feelings of insecurity, low self-esteem, and anxiety. Another issue is cyberbullying, which is harassment that many young adults experience online, which further affects their psychosocial well-being. The study also shows that social media use, mainly the ones used late at night, does result in sleep disturbances and higher stress levels, mainly attributed to Fear of Missing Out (FOMO). However, social media is helpful for adolescents. In many young adults, social media allows the sensation of existence, offers supportive speech, and is even helpful for self-presentation. Some of them also pointed to the reasons why they use social networks: they like to communicate with people who think alike or look for content related to mental disorders, which makes them feel not so lonely. Nonetheless, in the research, the Pakistani cultural environment is equally valid, where self-esteem, honor, and social recognition count more. Even these cultural frameworks may be of greater interest than learning about young people’s use of social media networks and how this social networking shapes the adolescent youths’ approach to mental health and how they connect with their peers virtually. More crucially, the findings of this study improve our understanding of the threats and positioning of social networks as well as making suggestions on how the social network misuse can be managed. The research attempts to raise these issues in order to alleviate the harmful effects of social media but also enhance its positive role among the mental health of Pakistan’s youth.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1951
by Maria Verrou, Dimitris D. Vlastos, Paraskevi Theofilou
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.4, No.1, 2025;
Divorce has increased dramatically in recent decades. Many separated parents adopt the “bird nesting” technique, where the parents rotate on a weekly basis in the family home, allowing the children to remain in their familiar environment. Thus, the present study investigated the correlation of “bird nesting” with the parents’ mental resilience. For this purpose, questionnaires were used on a sample of 99 parents who have divorced in the last 2 years, where they were asked about their demographic characteristics as well as questions related to the use of the “bird nesting” technique and mental resilience. The results showed that no statistically significant difference was found in mental resilience between parents who apply and do not apply the “bird nesting” technique. Overall, the present research did not find a relationship between the use of the “bird nesting” technique and the mental resilience of divorced parents. It is possible that the relationship is affected by various factors, such as the duration of the divorce, the age of the children, the financial situation, the existence of new partners, etc.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1442
by Alice Vo Edwards, Gavin MacDonald, William Abraczinskas
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.4, No.1, 2025;
In this study; we analyzed the relationship between U.S. workers’ reported levels of ADHD symptomatology and the impact of pandemic conditions on symptomatic impairment and the estimated prevalence of Adult ADHD. We compared data from the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale Screener (ASRS) collected during the pandemic with data from two pre-pandemic studies. Our findings indicate that during the pandemic; mean impairment scores on all six ASRS items increased; leading to a predicted rise in the Adult ADHD diagnosis rate to 9.26%; compared to the pre-pandemic estimate of 4.4%. These results suggest that more adults experienced significant ADHD-related challenges during the pandemic. As organizations continue to implement remote work and other pandemic-related changes; it is important to consider the unique difficulties that neurodiverse workers; particularly those with ADHD; may face in adapting to these new work environments.
 Open Access
Open Access
Article
Article ID: 1773
by Alan Johnston
Applied Psychology Research, Vol.4, No.1, 2025;
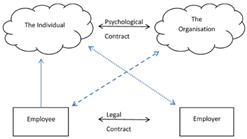
Many would argue that much of the higher education sector is reliant on goodwill, including the willingness to work with and support colleagues in the fulfilment of the fundamental roles associated with being an academic, this research suggests that a fundamental part of this is reliant on how the individual’s psychological contract manifests into academic citizenship. Research into the psychological contract of academics is limited. Similarly, there is also limited research into the concept of academic citizenship. This paper considers the concept of academic citizenship through the lens of the psychological contract, suggesting the notion of academic citizenship is borne out of the employment in and the perception of the academic role. The research made use of an interpretivist design using a series of semi-structured interviews. Following a qualitative base the study draws on the lived experiences of eighteen Business School academics across nine Universities. Using thematic analysis to draw out key themes and linkages, the research provides an overview of the employment relationship with employers and colleagues. The paper provides an understanding of individual behaviour in the workplace which is crucial to effective performance management and employee engagement. As such this paper contributes to understanding academics within the workplace and their responses to the behaviour of others. The research brings together two constructs which have not previously been considered, noting the inter-relationship between the two.