Predicting manipulated regions in deepfake videos using convolutional vision transformers
Abstract
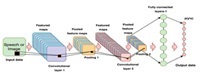
Deepfake technology, which uses artificial intelligence to create and manipulate realistic synthetic media, poses a serious threat to the trustworthiness and integrity of digital content. Deepfakes can be used to generate, swap, or modify faces in videos, altering the appearance, identity, or expression of individuals. This study presents an approach for deepfake detection, based on a convolutional vision transformer (CViT), a hybrid model that combines convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs). The proposed study uses a 20-layer CNN to extract learnable features from face images, and a ViT to classify them into real or fake categories. The study also employs MTCNN, a multi-task cascaded network, to detect and align faces in videos, improving the accuracy and efficiency of the face extraction process. The method is assessed using the FaceForensics++ dataset, which comprises 15,800 images sourced from 1600 videos. With an 80:10:10 split ratio, the experimental results show that the proposed method achieves an accuracy of 92.5% and an AUC of 0.91. We use Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) visualization that highlights distinctive image regions used for making a decision. The proposed method demonstrates a high capability of detecting and distinguishing between genuine and manipulated videos, contributing to the enhancement of media authenticity and security.
References
[1]Karnouskos S. Artificial Intelligence in Digital Media: The Era of Deepfakes. IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society. 2020; 1(3): 138-147. doi: 10.1109/tts.2020.3001312
[2]Grobler GD. Narrative strategies in the creation of animated poetry-film [PhD thesis]. University of South Africa; 2021.
[3]Wodajo D, Atnafu S, Akhtar Z. Deepfake video detection using generative convolutional vision transformer. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.07036 (accessed on 20 May 2024).
[4]Heidari A, Jafari Navimipour N, Dag H, et al. Deepfake detection using deep learning methods: A systematic and comprehensive review. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. 2023; 14(2). doi: 10.1002/widm.1520
[5]Kearns L, Alam A, Allison J. Synthetic media authentication threats: Detection using a combination of neural network and blockchain technology. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4658121 (accessed on 20 May 2024).
[6]Chesney R, Citron DK. Deep Fakes: A Looming Challenge for Privacy, Democracy, and National Security. SSRN Electronic Journal. 2018. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3213954
[7]Masood M, Nawaz M, Malik KM, et al. Deepfakes generation and detection: state-of-the-art, open challenges, countermeasures, and way forward. Applied Intelligence. 2022; 53(4): 3974-4026. doi: 10.1007/s10489-022-03766-z
[8]Montserrat DM, Hao H, Yarlagadda SK, et al. Deepfakes Detection with Automatic Face Weighting. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW); 2020. doi: 10.1109/cvprw50498.2020.00342
[9]Afchar D, Nozick V, Yamagishi J, et al. MesoNet: a Compact Facial Video Forgery Detection Network. In: 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS); 2018. doi: 10.1109/wifs.2018.8630761
[10]Ha H, Kim M, Han S, et al. Robust Deep Fake Detection Method based on Ensemble of ViT and CNN. In: Proceedings of the 38th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing; 2023. doi: 10.1145/3555776.3577769
[11]Hasan FS. FaceForensics-1600 videos-preprocess. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/farhansharukhhasan/faceforensics1600-videospreprocess?rvi=1 (accessed on 23 May 2024).
[12]Jose EMG, Haridas MTP, Supriya MH. Face Recognition based Surveillance System Using FaceNet and MTCNN on Jetson TX2. 2019 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Systems (ICACCS). Published online March 2019. doi: 10.1109/icaccs.2019.8728466
[13]Selvaraju RR, Cogswell M, Das A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); 2017; Venice, Italy. pp. 618-626. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.74
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohan Bhandari, Sushant Shrestha, Utsab Karki, Santosh Adhikari, Rajan Gaihre

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.