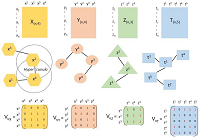
The Markov chain of Hidden Markov Model of interaction of the K-RAS4B proteins in catalytic environment with lipid membranes has a Hilbert measure
Abstract
A Hidden Markov Model containing both stationary Markov processes and time-varying Markov processes is considered: the corresponding Markov chain is newly proven to be one whose transition operators are on a space with Hilbert metric (whose measure exists and is unique). The Markov chain is therefore newly proven to be one with bounded moments. The further mathematical developments are envisaged. Applications are newly given for the analytical expressions of description of allosteric systems. The model of interaction of the K-RAS4B proteins with lipid membranes is newly considered accordingly; new drug design is explained.
References
[1]López CA, Agarwal A, Van QN, et al. Unveiling the Dynamics of KRAS4b on Lipid Model Membranes. The Journal of Membrane Biology. 2012; 254: 201.
[2]Prakash P, Gorfe AA. Lessons from computer simulations of RAS proteins in solution and in membrane, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013; 1830, 211-5218.
[3]Cao S, Chung S, Kim SJ, et al. K-Ras G-domain binding with signaling lipid phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-phosphate (PIP2): membrane association, protein orientation, and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2019; 294: 7068-7084.
[4]Erwin N, Patra S, Dwivedi M, et al. Influence of isoform-specific RAS lipidation motifs on protein partitioning and dynamics in model membrane systems of various complexity. Biol. Chem. 2017; 398: 547-563.
[5]Kapoor S, Weise K, Erlkamp M, et al. The role of G-domain orientation and nucleotide state on the RAS isoformspecific membrane interaction. Eur. Biophys. J. 2012; 41: 801-813.
[6]Weise K, Kapoor S, Denter C, et al. Membranemediated induction and sorting of K-RAS microdomain signaling platforms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011; 133: 880-887.
[7]Werkmuller A, Triola G, Waldmann H, et al. Rotational and translational dynamics of RAS proteins upon binding to model membrane systems. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2013; 14: 3698-3705.
[8]Chakrabarti M, Jang H, Nussinov R. Comparison of the conformations of KRAS isoforms, K-RAS4A and K-RAS4B, points to similarities and significant differences. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2016; 120: 667-679.
[9]Li S, Jang H, Zhang J, et al. Raf-1 cysteine-rich domain increases the affinity of K-RAS/Raf at the membrane, promoting MAPK signaling. Structure 2018; 26: 513-525e2.
[10]Mazhab-Jafari MT, Marshall CB, Smith MJ, et al. Oncogenic and RASopathy-associated K-RAS mutations relieve membrane-dependent occlusion of the effector-binding site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015; 112: 6625-6630.
[11]McCarthy M, Prakash P, Gorfe AA. Computational allosteric ligand binding site identification on RAS proteins, Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016; 48: 3-10.
[12]Prakash P, Zhou Y, Liang H, et al. Oncogenic K-RAS binds to an anionic membrane in two distinct orientations: a molecular dynamics analysis. Biophys. J. 2016; 110: 1125-1138.
[13]Travers T, Lopez CA, Van QN, et al. Molecular recognition of RAS/RAF complex at the membrane: role of RAF cysteine-rich domain. Sci. Rep. 2018; 8: 8461.
[14]Hancock JF. RAS proteins: different signals from different locations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol 2003; 4: 73-385.
[15]Hobbs GA, Der CJ, Rossman KL. RAS isoforms and mutations in cancer at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 2016; 129 (7): 1287-1292.
[16]Ntai I, Fornelli L, DeHart CJ, et al. Precise characterization of KRAS4B proteoforms in human colorectal cells and tumors reveals mutation/ modification cross-talk. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018; 115(16): 4140-4145.
[17]Nussinov R, Tsai CJ, Jang H. Oncogenic RAS isoforms signaling specificity at the membrane. Cancer Res 2018; 78: 593–602.
[18]Cholewa M, Gomb P. Deciding of HMM parameters based on number of critical points for gesture recognition from motion capture data. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1110.6287.pdf. (accessed on 2 March 2024).
[19]Cholewa M, Gomb MP. Estimation of the number of states for gesture recognition with Hidden Markov Models based on the number of critical points in time sequence. Pattern Recognition Letters 2013; 34: 574-579.
[20]Prakash, P, Gorfe, AA. Probing the conformational and energy landscapes of KRAS membrane orientation. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2019; 123: 8644-8652.
[21]Hartigan JA, Wong MA. Algorithm AS 136: a K-means clustering algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1979; 28: 100–108.
[22]Deuflhard P, Weber M. Robust Perron cluster analysis in conformation dynamics. Linear Algebra Appl. 2005; 398: 161–184.
[23]Castelli M. Decrypting Allostery in Membrane-Bound K-Ras4B Using Complementary ’In Silico’ Approaches Based on Unbiased Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023; 146: 901-919.
[24]Weise K. Dissociation of the K-Ras4B/PDEδ Complex upon Contact with Lipid Membranes: Membrane Delivery Instead of Extraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012; 134: 11503.
[25]Petrie T. Probabilistic functions of finite-state Markov chains. PNAS 1967; 57(3): 580-581.
[26]Baum LE, Petrie T, Soules G, et al. A Maximization Technique Occurring in the Statistical Analysis of Probabilistic Functions of Markov Chains. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 1970; 41: 164-171.
[27]Jenkinson O. Ergodic optimization. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems. AIMS 2006; 15: 197-224.
[28]Hartigan JA, Wong MA. A K-Means Clustering Algorithm: Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series C (Applied Statistics). 1979; 28: 100-108.
[29]Hartigan JA. Clustering Algorithms. New York: Wiley; 1975.
[30]Di Masi GB, Stettner LH. Ergodicity of hidden Markov models. Control Signals Systems. Spring publishing; 2005; 17: 269-296.
[31]Liverani C. Decay of Correlations. Annals of Mathematics Second Serie. 1995; 142(2): 239-301.
[32]Akaike H. Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In: Petrov BN, Csáki F (editors). Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Information Theory; 2–8 September 1971; Tsahkadsor, Armenia. Springer-Verlag; 1992: 610-624.
[33]Sinai Ya.G. Construction of Markov partitions. Functional Analysis and Its Applications. Springer publishing; 1968; 2: 61-82.
[34]Banerjee A, Jang H, Nussinov R, et al. The disordered hypervariable region and the folded catalytic domain of oncogenic K-Ras4B partner in phospholipid binding. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016; 36: 10-17.
[35]Chen P, Liu R, Li Y, et al. Detecting critical state before phase transition of complex biological systems by hidden Markov model. Bioinformatics. 2016; 32(14): 2143.
[36]Shrestha R, Chen D, Frank P, et al. Recapitulation of cell-like KRAS4b membrane dynamics on complex biomimetic membranes. Science 2021; 25(1): 103608
[37]Metzler R, Jeon JH, Cherstvy AG. Non-Brownian diffusion in lipid membranes: Experiments and simulations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1858(10): 2451.
[38]Khaled M, Gorfe A. Sayyed-Ahmad A. Conformational and Dynamical Effects of Tyr32 Phosphorylation in K-Ras: Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Markov State Models Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2019; 123(36): 7667-7675.
[39]Lu HX, Hu ZY, Faraudo J, et al. Discovery of a novel drug using lipid-based formulation targeting G12D-mutated KRAS4B through non-covalent bonds. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.05.535682.
[40]Lu HX, Hu ZY, Faraudo J, et al. In silico design of a lipid-like compound targeting KRAS4B-G12D through noncovalent bonds. Nanoscale. 2023; 15, 19359-19368.
[41]Holewijn PJ, Hordijk A. On the convergence of moments in stationary Markov chains. Stochastic Processes and Their Applications. 1975; 3: 55-64.
[42]Bertail P, Clémencon S. Sharp bounds for the tails of functionals of Markov chains. Theory of Probability and its Applications. 2010; 54: 505–515.
[43]Dobrushin R.L. Central limit theorem for nonstationary Markov chains. I, Theory of Probability & and Its Applications. SIAM Publishing; 1956.
[44]Steinsaltz D. Convergence of moments in a Markov-chain central limit theorem, Indagationes Mathematicae Publishing; 2001.
[45]Kartashov M. The asymptotic behavior of rare Markov moments defined on time inhomogeneous Markov chains. Theory of Probability and Mathematical Statistics Publishing; 2014.
[46]Naor A, Rao S, Regev O. Concentration of Markov chains with bounded moments, Ann. Inst. H. Poincaré Probab. Statist. 2020; 56: 2270-2280.
[47]Ki-Young L, Mitsuhiko I, Marshall CB. The Self-Association of the KRAS4b Protein is Altered by Lipid-Bilayer Composition and Electrostatics. Angewantde Chimie International Edition Publishing. 2023; 62: e202218698.
[48]Shrestha, R, Carpenter, TS, Van, QN, et al. Membrane lipids drive formation of KRAS4b-RAF1 RBDCRD nanoclusters on the membrane. Commun Biol 2024; 7: 242.
[49]Sarkar S, Goswami D. Lifetime of actin-dependent protein nanoclusters. Biophysical Journal. 2023; 122(2): 290-300.
[50]Shree S. Revealing KRas4b topology on the membrane surface. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2023; 678: 122-127.
[51]Lee KY. Two Distinct Structures of Membrane-Associated Homodimers of GTP- and GDP-Bound KRAS4B Revealed by Paramagnetic Relaxation Enhancement. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020; 59: 11037-11045.
[52]Ngo VA, Sarkar S, Neale C, et al. How Anionic Lipids Affect Spatiotemporal Properties of KRAS4B on Model Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2020; 124: 5434-5453.
[53]Gu X, Liu D, Yu YK, et al. Quantitative Paramagnetic NMR-Based Analysis of Protein Orientational Dynamics on Membranes: Dissecting the KRas4B-Membrane Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023; 145: 10295-10303.
[54]Lu H. In silico design of a lipid-like compound targeting KRAS4B-G12D through non-covalent bonds. Nanoscale. 2023; 15: 19359-19368.
[55]Angela P, Sofia C, Alessandra M. Molecular dynamics simulations for the structure-based drug design: targeting small-GTPases proteins. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery 2024; 6: 1-21.
[56]Lu HX, Hu ZY, Faraudo J, et al. Discovery of a novel drug using lipid-based formulation targeting G12D-mutated KRAS4B through non-covalent bonds e-print. BioRxiv; 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.04.05.535682
Copyright (c) 2024 Orchidea Maria Lecian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.