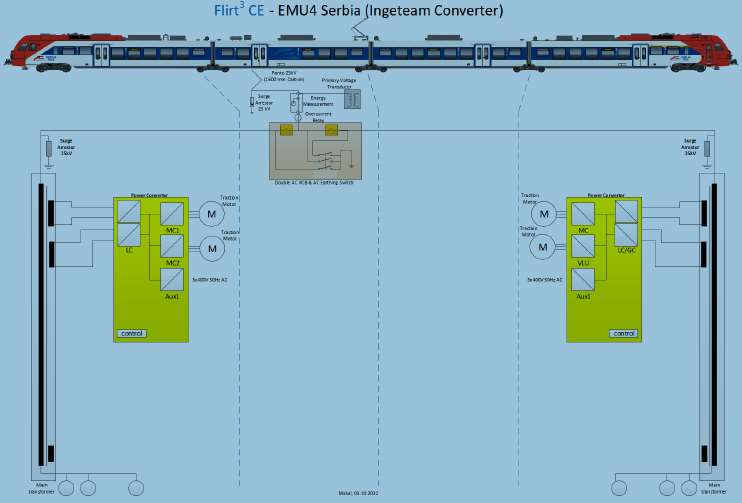
Traction drive simulations when starting an electric locomotive series ŽS 444 on the railway tracks of Serbia
Abstract
The manuscript presents and describes the Model in Matlab-simulink, which allows to display the time change of the firing angle of the thyristor of the single-phase rectifier, the mean value of the voltage, the armature current and the speed of the electric motor during the start-up of the electric locomotive ŽS 444 series for different given mechanically loaded and reference speeds of traction electric motors. The model makes it possible to establish the desired reference speed change ramps for different reference speeds and mechanical loads from +250 rpm, i.e., the maximum current of the electric motor armature up to 1250 A.
References
[1]Milićević Z, Aranđelović D, Marjanović V, Pejčić D. Electric locomotives JŽ 441 series. Želnid, Belgrade; 1997.
[2]Dragan B. Rajković: Contribution to the analysis of axle breakage on locomotives series 441, 461 and 444. In: Proceedings of the XIV ŽELKON '10 Niš; 2010.
[3]Vabić V, Grašković I. Course for service personnel of locomotive series JŽ 444 and JŽ 461-200 sedries, Končar-električne lokomotive dd., document number GO5926, archive location 211-0103. Zagreb; 2005.
[4]Branislav G. Research and Analysis in the Electric Traction System of the Serbian Railways. Eliva Press; 2023.
[5]Boldea I, Nasar SA. Electric Drives. CRC Press; 2016. doi: 10.1201/9781315368573
[6]Nondahl, Thomas A. Microprocessor Control of Motor Drives and Power Converters, tutorial course. IEEE Industry Application Society; 1993,
[7]Bolton W. Mechatronics: Electronic Control Systems in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, 3rd ed. Pearson Education; 2004.
[8]Harpreet Kaur. Electric drives and their controlling techniques. Scholar's press London; 2019.
[9]Mohan N, Raju S. Analysis and Control of Electric Drives: Simulations and Laboratory Implementation. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2021.
[10]Merabet A. Advanced Control Systems for Electric Drives. Electronics; 2021. doi: 10.3390/books978-3-03943-700-9
[11]Dorji C. Review Of Electric Motor Drives. Machine Drives and control; 2015. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.1.1198.6408
[12]Golnaraghi F, Kuo BC. Automatic Control Systems, 9th ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2010.
[13]Kryukov OV, Blagodarov DA, Dulnev NN, et al. Intelligent Control of Electric Machine Drive Systems. In: Proceedings of the 2018 X International Conference on Electrical Power Drive Systems (ICEPDS); 2018.
[14]Hughes A. Electric Motors and Drives—Fundamentals, Types and Applications, 3rd ed. Elsevier, Oxford, UK; 2006.
[15]Schröder D. Elektrische Antriebe—Grundlagen, 3rd ed. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2007.
[16]Jauch C, Tamilarasan S, Bovee K, et al. Modeling for drivability and drivability improving control of HEV. Control Engineering Practice. 2018; 70: 50-62. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2017.09.014
[17]Ramachandran N, Sivasubramanian R, Palanivel R, et al. Design and Fabrication of Hybrid Mobility Scooter. Advances in Materials Research; 2021.
[18]Omar AMS, Samat AAA, Isa SSM, et al. New model of inverting substation for DC traction with regenerative braking system. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2017; 1875: 030016. doi: 10.1063/1.4998387
[19]Barna G. Simulation model of a series DC motor for traction rail vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR); 2016.
[20]Wang X, Peng T, Wu P, et al. Influence of electrical part of traction transmission on dynamic characteristics of railway vehicles based on electromechanical coupling model. Scientific Reports. 2021; 11(1). doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97650-4
[21]Goolak S, Tkachenko V, Bureika G, et al. Method Of Spectral Analysis Of Traction Current Of Ac Electric Locomotives. Transport. 2021; 35(6): 658-668. doi: 10.3846/transport.2020.14242
[22]Litovchenko VV, Nazarov DV, Sharov VA. Simulation Model of a Direct-Current Electric Locomotive with Commutator Traction Motors. Russian Electrical Engineering. 2020; 91(1): 69-76. doi: 10.3103/s1068371220010071
[23]Goolak S, Sapronova S, Tkachenko V, et al. Improvement of the model of power losses in the pulsed current traction motor in an electric locomotive. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies. 2020; 6(5 (108)): 38-46. doi: 10.15587/1729-4061.2020.218542
[24]Chiriac G, Nituca C, Sticea D. Electric Locomotive Laboratory Test Bench for Research and Educational Purposes. 2019 8th International Conference on Modern Power Systems (MPS). Published online May 2019: 1-4. doi: 10.1109/mps.2019.8759652
[25]Goolak S, Yermolenko E, Tkachenko V, et al. Determination of voltage at the rectifier installation of the electric locomotive VL-80K for each position of the controller driver’s. Technology audit and production reserves. 2022; 1(1(63)). doi: 10.15587/2706-5448.2022.251947
[26]Goolak S, Riabov I, Tkachenko V, Yeritsyan B. Simulation model of traction electric drive of AC electric locomotive equipped with collector electric motors. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny. 2023; 1(4): 120-129. doi: 10.15199/48.2023.04.21
Copyright (c) 2024 Branislav Gavrilovic, Vladimir Aleksandrovich Baboshin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




.png)