A study on membrane enzyme Na+-K+-ATPase in lindane exposed fish, Channa punctatus
Abstract
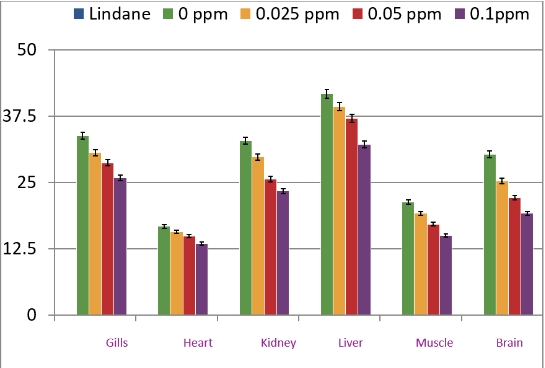
Na+-K+-ATPase is a membrane-bound enzyme responsible for the transport of ions through the membrane and the immediate release of energy. This enzyme is known to be an early target for oxygen radical-induced damage to intact cells. Exposure of C. punctatus to subacute concentrations of lindane for 96 h caused a significant reduction in the activities of Na+-K+-ATPase in all the tissues of the fish tested, with the brain being maximally affected and the heart being the least affected organ at the highest concentration of lindane (0.1 mg/L). The effect of pesticides was concentration-dependent. The percent decrease in the activity of Na+-K+-ATPase in brain, gills, heart, kidney, liver, and muscle was found to be 36.7, 23.4, 19.2, 29, 22.9, and 29.7, respectively. The order of level of enzyme activity recorded was as follows: liver > gills > kidney > brain > muscle > heart in the control.
References
[1]Gupta A, Rai DK, Pandey RS, et al. Analysis of some heavy metals in the riverine water, sediments and fish from river Ganges at Allahabad. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 2008; 157(1-4): 449-458. doi: 10.1007/s10661-008-0547-4
[2]German AV, Zakonnov VV, Mamontov AA. Organochlorine compounds in bottom sediments, benthos, and fish in the volga pool of the Rybinsk Reservoir. Water Resources. 2010; 37(1): 84-88. doi: 10.1134/s0097807810010082
[3]Gupta MA. A Case Study on the Bioaccumulated Organochlorines in Fish Related to their inhabitant Res. Rev. J Ecol. Environ. 2021; 9(5).
[4]Gupta A, Sharma B. Evaluation of Levels of Phosphatases in the Lindane Exposed Fish, Channa punctatus. Journal of Biomedical Research & Environmental Sciences. 2023; 4(3): 555-561. doi: 10.37871/jbres1710
[5]Jackson DA, Gardner DR. The effects of some organochlorine pesticide analogs on salmonid brain ATPases. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 1973; 2(4): 377-382. doi:10.1016/0048-3575(73)90049-7
[6]Gupta A, Siddiqi NJ, Sharma B. Bioaccumulation and Biochemical Studies of Toxicants in Fish on AChE. Open J Pathol Toxicol Res. 2021; 1(1).
[7]Gupta A, Sharma B. Acute Chronic Toxicity of Lindane in Channa punctatus. Open J Pathol Toxicol Res. 2021; 1(1).
[8]Gupta A. An Evaluation of Lactate Dehydrogenase in the Lindane. International Journal of Animal Biotechnology and Applications. 2021; 7(1): 2455-7315.
[9]Austin B. The effects of pollution on fish health. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 1998; 85(S1): 234S-242S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1998.tb05303.x
[10]Zimmer AM, Perry SF. Physiology and aquaculture: A review of ion and acid‐base regulation by the gills of fishes. Fish and Fisheries. 2022; 23(4): 874-898. doi: 10.1111/faf.12659
[11]Garcia Parra J, Baldisserotto B. Effect of Water pH and Hardness on Survival and Growth of Freshwater Teleosts. In: Baldisserotto B (editor). Fish Osmoregulation. Boca Raton; 2007. pp. 135-150. doi: 10.1201/b10994-6
[12]Almeida CL, Aguiar LH, Moraes G. Effect of methyl parathion on the muscle and brain acetylcholinesterase activity of matrinxã (Brycon cephalus). Ciência Rural. 2005; 35(6): 1412-1416. doi: 10.1590/s0103-84782005000600029
[13]Metcalf RL. Pesticides in Aquatic Environments. Springer US; 1977. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2868-1
[14]Lucu Č, Towle DW. Na++/K+-ATPase in gills of aquatic crustacea. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 2003; 135(2): 195-214. doi: 10.1016/s1095-6433(03)00064-3
[15]Thorsen K, Drengstig T, Ruoff P. Transepithelial glucose transport and Na+/K+ homeostasis in enterocytes: An integrative model. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2014; 307(4): C320-C337. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00068.2013
[16]Nie Y, Bai F, Chaudhry MA, et al. The Na/K-ATPase α1 and c-Src form signaling complex under native condition: A crosslinking approach. Scientific Reports. 2020; 10(1). doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61920-4
[17]Pivovarov AS, Calahorro F, Walker RJ. Na+/K+-pump and neurotransmitter membrane receptors. Invertebrate Neuroscience. 2018; 19(1). doi: 10.1007/s10158-018-0221-7
[18]Mernissi G, Barlet-Bas C, Khadouri C, et al. Characterization and localization of ouabain-insensitive Na-dependent ATPase activities along the rat nephron. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991; 1064(2): 205-211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90303-P
[19]Jimenez T, McDermott JP, Sánchez G, et al. Na/K-ATPase α4 isoform is essential for sperm fertility. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010; 108(2): 644-649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016902108
[20]Clausen MV, Hilbers F, Poulsen H. The Structure and Function of the Na/K-ATPase Isoforms in Health and Disease. Frontiers in Physiology. 2017; 8. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00371
[21]Attwell D, Laughlin SB. An Energy Budget for Signaling in the Grey Matter of the Brain. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2001; 21(10): 1133-1145. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200110000-00001
[22]Lei J, Nowbar S, Mariash CN, et al. Thyroid hormone stimulates Na-K-ATPase activity and its plasma membrane insertion in rat alveolar epithelial cells. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2003; 285(3): L762-L772. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00376.2002
[23]Pirahanchi Y, Jessu R, Aeddula NR. Physiology, Sodium Potassium Pump. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537088/ (accessed on 13 June 2024).
[24]Mercer RW, Biemesderfer D, Bliss DP, et al. Molecular cloning and immunological characterization of the gamma polypeptide, a small protein associated with the Na/K-ATPase. The Journal of cell biology. 1993; 121(3): 579-586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.579
[25]Martinez NP, Pinch M, Kandel Y, et al. Knockdown of the Sodium/Potassium ATPase Subunit Beta 2 Reduces Egg Production in the Dengue Vector, Aedes aegypti. Insects. 2023; 14(1): 50. doi: 10.3390/insects14010050
[26]Kjeldsen K. Myocardial Na/K-ATPase: Clinical aspects. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2003; 8(3): 131-133.
[27]Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AI, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with Folin-Phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951; 193: 265-275. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
[28]Svobaca P, Mossinger B. Catecholamine and brain microsomal Na+/K+-ATPase-1, protection against lipoperoxidative damages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981; 30: 427-432. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90626-2
[29]Fiske CH, Subbarow Y. Colourimetric determination of phosphorous. J Biol. Chem. 1925; 66: 375-400. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)84756-1
[30]Kim MS, Akera T. O2 free radicals: cause of ischemia-reperfusion injury to cardiac Na+-K+-ATPase. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 1987; 252(2): H252-H257. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.2.h252
[31]Kako K, Kato M, Matsuoka T, et al. Depression of membrane-bound Na+-K+-ATPase activity induced by free radicals and by ischemia of kidney. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 1988; 254(2): C330-C337. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.2.c330
[32]Sharma RM. Effect of endosulfan on adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activity in liver, kidney, and muscles of Channa gachua. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 1988; 41(3): 317-323. doi: 10.1007/bf01688873
[33]Ozcan Oruc E, Uner N, Tamer L. Comparison of Na+-K+-ATPase Activities and Malondialdehyde Contents in Liver Tissue for Three Fish Species Exposed to Azinphosmethyl. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2002; 69(2): 271-277. doi: 10.1007/s00128-002-0057-y
[34]Prashanth MS, David M. Impact of Cypermethrin on Na+-K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ ATPases in Indian Major Carp, Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2009; 84(1): 80-84. doi: 10.1007/s00128-009-9864-8
[35]Kumar A, Sharma B, and Pandey RS. Toxicoogical assessment of the pyrethroids insecticides with special reference to cypermethrin and λ-cyalothrin in fresh water fishes. Int. J. Biol. Med Res. 2010; 1(4): 315-325.
[36]Oluah NS, Mgbenka BO, Nwani CD, et al. Tissue-specific changes in Ca2+-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase activities in freshwater African catfish Clarias gariepinus juvenile exposed to oxadiazon. The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology. 2020; 81(1). doi: 10.1186/s41936-020-00186-8
[37]Marx MTS, Souza C de F, Almeida APG, et al. Expression of Ion Transporters and Na+/K+-ATPase and H+-ATPase Activities in the Gills and Kidney of Silver Catfish (Rhamdia quelen) Exposed to Different pHs. Fishes. 2022; 7(5): 261. doi: 10.3390/fishes7050261
[38]Esbaugh AJ, Brix KV, Grosell M. Na+/K+-ATPase isoform switching in zebrafish during transition to dilute freshwater habitats. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2019; 286(1903): 20190630. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.0630
[39]McCormick SD, Regish AM, Christensen AK. Distinct freshwater and seawater isoforms of Na+/K+-ATPase in gill chloride cells of Atlantic salmon. Journal of Experimental Biology. 2009; 212(24): 3994-4001. doi: 10.1242/jeb.037275
[40]Yang WK, Hsu AD, Kang CK, et al. Intestinal FXYD12 and sodium-potassium ATPase: A comparative study on two euryhaline medakas in response to salinity changes. PLOS ONE. 2018; 13(7): e0201252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201252
[41]Maiti AK, Paul G, Maity B, et al. Chromium III Exposure Inhibits Brain Na+/K+-ATPase Activity of Clarias batrachus L. Involving Lipid Peroxidation and Deficient Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Activity. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2009; 83(4): 479-483. doi: 10.1007/s00128-009-9827-0
[42]Gupta A, Sharma B. A study on Transaminases in Lindane Exposed Fish C. punctatus. Journal of Biomedical Research & Environmental Sciences. 2023; 4(6): 1100-1107. doi: 10.37871/jbres1773
[43]Gupta A, Sharma B. Oxidative stress biomarkers in a living cell. MOJ Toxicol. 2023; 7(1): 38-43. doi: 10.15406/mojt.2023.07.00176
[44]Gupta A. A Study on Analysis of Water Quality of Two Rivers Ganges and Yamuna. J Waste Manage Xenobio. 2023; 6(3): 000191.
[45]Gupta A, Sharma B. A review on water pollution by γHCH (lindane) and its removal using nanomaterials. Journal of Toxicological Studies. 2023; 1(1): 195. doi: 10.59400/jts.v1i1.195
[46]Lijnen P, Hespel P, Lommelen G, et al. Intracellular sodium, potassium and magnesium concentration, ouabain sensitive rubidium uptake and sodium efflux and Na+/K+ cotransport activity in erythrocytes of normal male subjects studied on two occasions. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1986; 8: 525-533.
Copyright (c) 2024 Aradhna Gupta, Bechan Sharma

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.